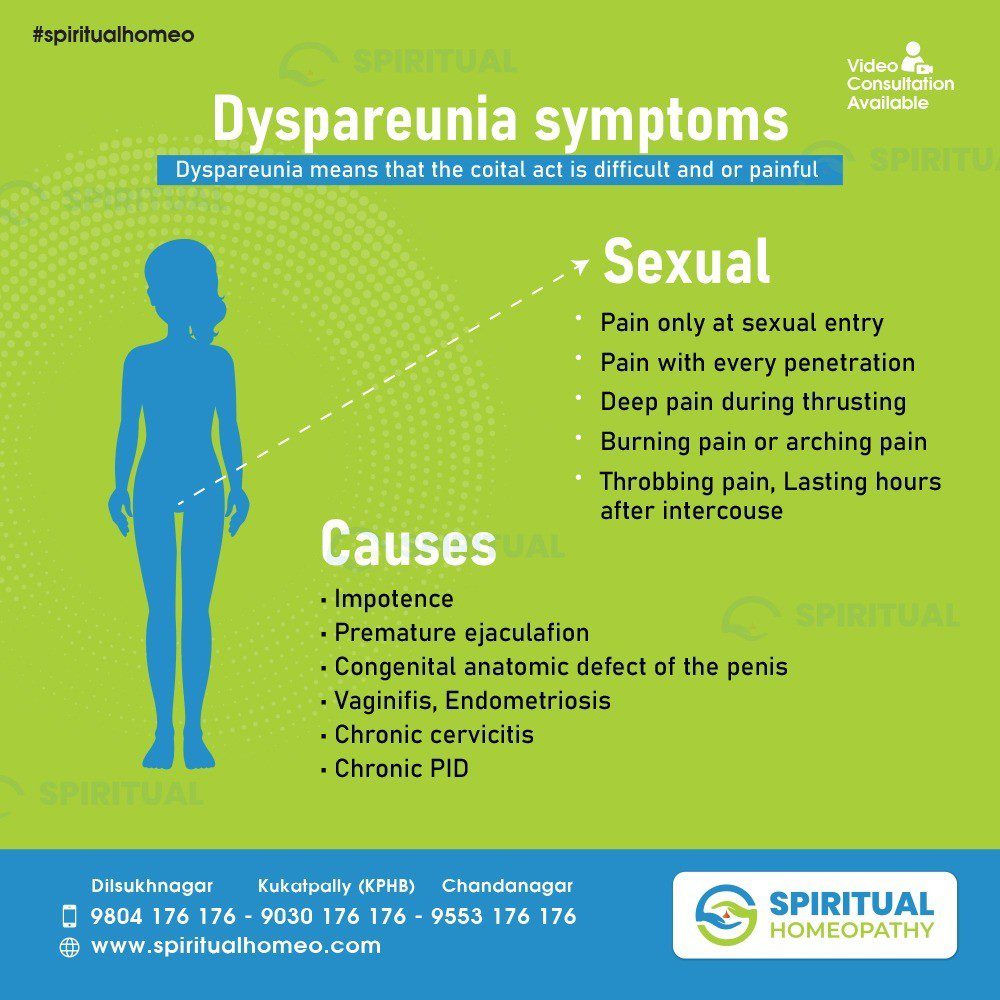
Dyspareunia refers to persistent or recurrent pain experienced during sexual intercourse. Both men and women can be affected by dyspareunia, and it can have various causes. Symptoms of dyspareunia may include:
Pain during penetration: Pain can occur at any point during sexual activity, including penetration, and it may be experienced as a sharp or burning sensation.
Pain with certain movements: The pain may be triggered by specific movements or positions during sexual intercourse.
Superficial or deep pain: Dyspareunia can manifest as pain at the entrance of the vagina (superficial dyspareunia) or deeper within the pelvis (deep dyspareunia).
Muscle spasms: In some cases, there may be involuntary muscle contractions or spasms in the pelvic floor muscles, contributing to pain during intercourse.
Burning or aching sensation: The pain may be described as a burning or aching sensation in the genital or pelvic region.
Pain after intercourse: Some individuals may experience pain after sexual activity has concluded.
Emotional distress: Dyspareunia can lead to emotional distress, anxiety, or fear related to sexual activity, potentially causing a decrease in sexual desire or avoidance of intimacy.
It’s important to note that the underlying causes of dyspareunia can vary and may include physical, psychological, or relational factors. Common physical causes in women include vaginal dryness, infections, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and certain gynecological conditions. In men, causes may include infections, prostatitis, and certain medical conditions affecting the genital region.
If someone is experiencing symptoms of dyspareunia, it is advisable to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional, such as a gynecologist or urologist, can perform a thorough evaluation, which may involve a physical examination, medical history review, and sometimes imaging studies or laboratory tests. Treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the pain and may include medications, counseling, or other interventions.