Homeopathy treatment for Diabetes
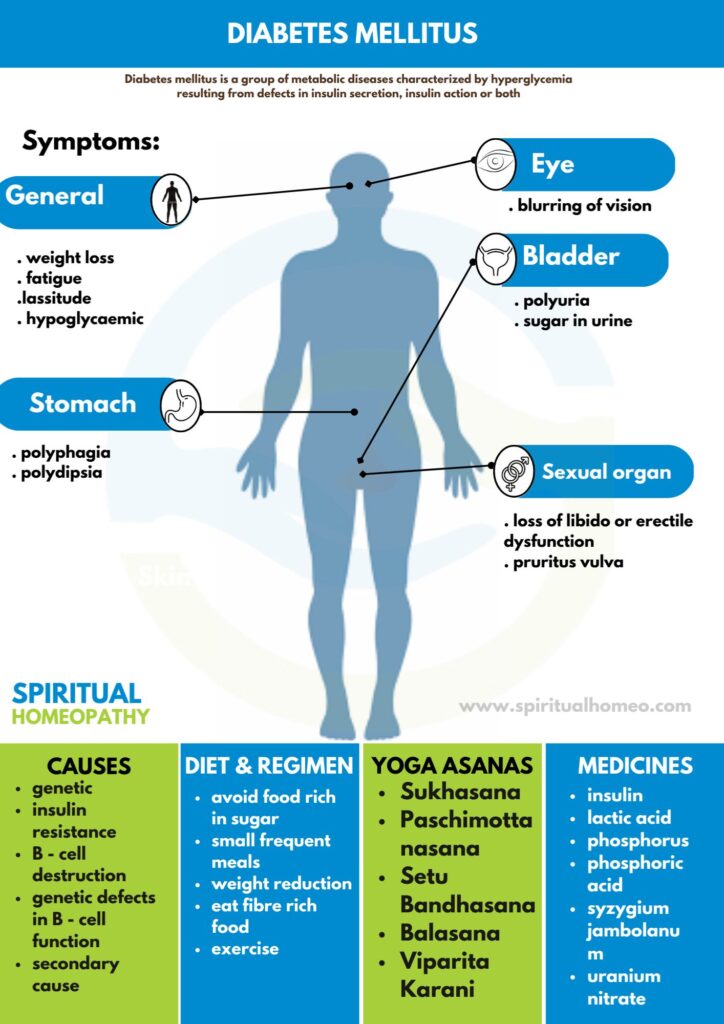
Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycaemia
resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action or both.
- Overview
- Causes
- Types
- Sign & Symptoms
- What to eat
- Diet and Regiment
- Homeopathic Treatment
- FAQ
- Reference
OVERVIEW
Diabetes mellitus is a disorder in which the amount of sugar in the blood is elevated. Doctors often use the full name diabetes mellitus, rather than diabetes alone, to distinguish this disorder from diabetes insipidus. Diabetes insipidus is a relatively rare disorder that does not affect blood glucose levels but, just like diabetes mellitus, also causes increased urination.
Blood sugar
Generally, the three major nutrients that make up most food are carbohydrates, proteins, and fat. Sugars are one of three types of carbohydrates, along with starch also fiber.
Moreover, There are many types of sugar. Some sugars are simple, and others are complex. Table sugar (sucrose) is made of two simpler sugars called glucose and fructose. Additionally, Milk sugar (lactose) is made of glucose and a simple sugar called galactose. The carbohydrates in starches, such as bread, pasta, rice, and similar foods, are long chains of different simple sugar molecules. Sucrose, lactose, carbohydrates, also other complex sugars must be broken down into simple sugars by enzymes in the digestive tract before the body can absorb them.
Besides this, Once the body absorbs simple sugars, it usually converts them all into glucose, which is an important source of fuel for the body. Glucose is the sugar that is transported through the bloodstream and taken up by cells. All in all, The body can also make glucose from fats and proteins. Blood “sugar” really means blood glucose.
Insulin
Basically, Insulin, a hormone released from the pancreas (an organ behind the stomach that also produces digestive enzymes), controls the amount of glucose in the blood. In detail, Glucose in the bloodstream stimulates the pancreas to produce insulin. Insulin helps glucose to move from the blood into the cells. Besides this, Once inside the cells, glucose is converted to energy, which is used immediately, or the glucose is stored as fat or the starch glycogen until it is needed. Lastly, The levels of glucose in the blood vary normally throughout the day.
Level of Glucose
They rise after a meal and return to pre-meal levels within about 2 hours after eating. In detail, Once the levels of glucose in the blood return to pre-meal levels, insulin production decreases. The variation in blood glucose levels is usually within a narrow range, about 70 to 110 milligrams per decilitre (mg/dL), or 3.9 to 6.1 millimoles per liter (mmol/L) of blood in healthy people. If people eat a large amount of carbohydrates, the levels may increase more. People older than 65 years tend to have slightly higher levels, especially after eating.
If the body does not produce enough insulin to move the glucose into the cells, or if the cells stop responding normally to insulin (called insulin resistance), the resulting high levels of glucose in the blood also the inadequate amount of glucose in the cells together produce the symptoms and complications of diabetes
CAUSES
- Insulin resistance
- Central obesity
- Predispose individuals to insulin resistance
- Abdominal fat is especially active hormonally, secreting a group of hormones called adipokines that may possibly impair glucose tolerance
-
Obesity is found in approximately 55% of patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes
- In the last decade, type 2 diabetes has increasingly begun to affect children and adolescents, likely in connection with the increased prevalence of childhood obesity
- Positive family history
TYPES
Etiological Classification of Diabetes mellitus and Impaired glucose tolerance
1.Type I DM (in other words; β-cell destruction, absolute insulin deficiency).
Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM)
(a) Autoimmune
(b) Idiopathic
2.Type II DM – Non-insulin dependent (in other words; NIDDM)
3. Maturity onset diabetes in young (in other words; MODY 1-6)
Genetic defects in β-cell function have the following
mutations:
- MODY 1 – Hepatocyte Nuclear Transcription factor (HNF) 4α
- MODY 2 – Glucokinase
- MODY 3 – HNF – 1α
- MODY 4 – Insulin promotor factor-1 (IPF1)
- MODY 5 – INF – 1β
- MODY 6 – Neurogenic differentiation1, (Neuro D1)
4.Secondary causes
a. Pancreatic disease i.e.
- Cystic fibrosis
- Trauma / pancreatopathy
- Hemochromatosis
- Pancreatitis
- Fibrocalcific pancreatic diabetes (in other words; FCPD)
- Carcinoma of pancreas
b. Endocrine disorder i.e.
- Acromegaly
- Cushing syndrome
- Glucagonoma
- Conn’s syndrome
- Pheochromocytoma
- Hyperthyroidism
c. Drug induced i.e.
- Glucocorticoids
- Diazoxide
- Thiazides
- Phenytoin
- Pentamidine
- Alpha Interferon
- Thyroid hormone
- Beta adrenergic
d. Infection i.e.
- Congenital
Rubella
- Coxsackie B virus
- Cytomegalovirus
e. Insulin Receptor Defect i.e.
- Anti-insulin Receptor Antibodies [in other words; Stiffman syndrome]
- Lipoatrophic Diabetes
f. Other Genetic syndrome associated with DM i.e.
- Down’s Syndrome
- Turner’s Syndrome
- Wolframe’s syndrome
- Prader willi syndrome
- Kline filters syndrome
- Porphyria
- Myotonic Dystrophy
- Laurence-Moon-Biedl syndrome
- Friedreich’s ataxia
5.Gestational diabetes
6.Impaired glucose tolerance (Borderline diabetes)
a. Primary: Obese, non-obese
b. Secondary: All conditions mentioned under secondary DM, cirrhosis of liver, kidney failure, chronic undernutrition, hypokalaemia, stress, e. g. myocardial infarction.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Usually gradual in adults, but acute in children.
Modes of presentation –
Presence of osmotic symptoms (i.e. polyuria, polyphagia, polydipsia)
- Weight loss, fatigue and lassitude
- Pruritus vulvae in females or balanitis in males
- Loss of libido or erectile dysfunction
- Blurring of vision
- Symptoms due to diabetes – related complications e.g., abdominal pain in ketoacidosis
Convulsions – Fits should be considered hypoglycaemic until proved otherwise, especially in children. EEG abnormalities are common in insulin-treated patients, especially those with recurrent hypoglycaemia. Day Time attacks suggest epilepsy, while nocturnal attacks are often hypoglycaemic.
WHAT TO EAT
For Diabetes Mellitus, a balanced diet helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Foods to Eat:
✅ High-fiber foods: Whole grains (oats, brown rice, quinoa), legumes, and vegetables improve blood sugar control.
✅ Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and broccoli are rich in nutrients and low in carbs.
✅ Healthy proteins: Lean meats, fish, eggs, tofu, and nuts help stabilize sugar levels.
✅ Healthy fats: Avocados, olive oil, and nuts reduce inflammation.
✅ Low-GI fruits: Berries, apples, pears, and guavas provide controlled sugar release.
✅ Dairy alternatives: Greek yogurt and skim milk in moderation.
Foods to Avoid:
❌ Refined carbs (white bread, pastries)
❌ Sugary drinks and sweets
❌ Fried and processed foods
Maintain portion control and eat small, frequent meals to manage sugar levels effectively. 🚀
DIET AND REGIMEN
- Restoration of normal blood glucose and optimal lipid levels.
- Maintenance of blood glucose level as near to physiologic levels to prevent onset or progression of complications.
- Maintenance of normal growth rate in children and adolescents as well as attainment and maintenance of reasonable body weight in adolescents and adults.
- Provision of adequate nutrition for pregnant women, the fetus and during lactation.
- Moreover, Consistency in timing of meals and snacks to prevent inordinate swings in blood glucose levels.
- Motivation to have small frequent meals.
- Determination of a meal plan appropriate for individual’s lifestyle and based on dietary history to have good compliance.
- Besides this, Management of weight reduction for obese individuals with NIDDM.
- Improvement in the overall health of patients with diabetes through optimal nutrition carbohydrates to the extent possible.
Why Choose Spiritual Homeopathy?
At Spiritual Homeopathy, we offer a unique approach to healing that integrates traditional homeopathic principles with a deep understanding of the spiritual aspects of health. Our team of experienced homeopathic practitioners combines expertise with empathy, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care tailored to your individual needs.
Our Approach to Treatment
We believe that true healing occurs when all aspects of a person—physical, emotional, and spiritual—are in balance. That’s why our treatment approach goes beyond simply addressing symptoms to identify and treat the underlying imbalances contributing to your health concerns. By addressing the root cause of illness and supporting your body’s innate healing ability, we empower you to achieve lasting health and vitality.
Services We Offer
Consultations: Our experienced best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad offer comprehensive consultations to assess your health concerns, medical history, and individual needs. we also take online consultation and We take the time to listen to your story, understand your unique health goals, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Remedies: At Spiritual Homeopathy, we provide a wide range of homeopathic remedies carefully selected to address a variety of health conditions. From acute ailments to chronic diseases, our remedies are safe, gentle, and effective, offering natural relief without the side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Follow-Up Care: We believe in the importance of ongoing support and monitoring throughout your healing journey. Our team is dedicated to providing regular follow-up care to track your progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that you are on the path to optimal health and well-being.
Our Commitment to You
At Spiritual Homeopathy, your health and wellness are our top priorities. We are committed to providing you with compassionate care, personalized treatment, and the support you need to achieve your health goals. Whether you are seeking relief from a specific health concern or simply looking to optimize your overall well-being, we are here to support you every step of the way.
FAQ
What is Diabetes Mellitus ?
Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycaemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action or both.
What causes Diabetes Mellitus ?
- β-cell destruction, absolute insulin deficiency
- Mutations: Glucokinase, HNF – 1α, Insulin promotor factor-1
- Pancreatic disease
- Endocrine disorder
- Drug induced
- Infection
- Insulin Receptor Defect
- Down’s Syndrome
- Turner’s Syndrome
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Diabetes Mellitus ?
- Uranium nitrate
- Syzygium jambolanum
- Phosphoric acid
- Phosphorus
- Lactic acid
- Bryonia
What are the symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus ?
- Polyuria, Polyphagia, also Polydipsia
- Weight loss, fatigue and lassitude
- Pruritus vulvae in females
- Balanitis in males
- Either Loss of libido or erectile dysfunction
- Blurring of vision
- Abdominal pain in ketoacidosis
What are the types of Diabetes Mellitus ?
- Type I DM
- Type II DM
- Maturity onset diabetes in young
- Secondary causes
- Gestational diabetes
- Impaired glucose tolerance
REFFERNCE
[1] Text book of medicine by Golwala
[2] Therapeutics from Zomeo ultimate LAN
[3]Diabetes Risk Factors | CDC
[4]Diabetes mellitus type 2 physical examination – wikidoc
[5]Differential Diagnosis | Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (osu.edu)
[6]How to Prevent Diabetes: MedlinePlus