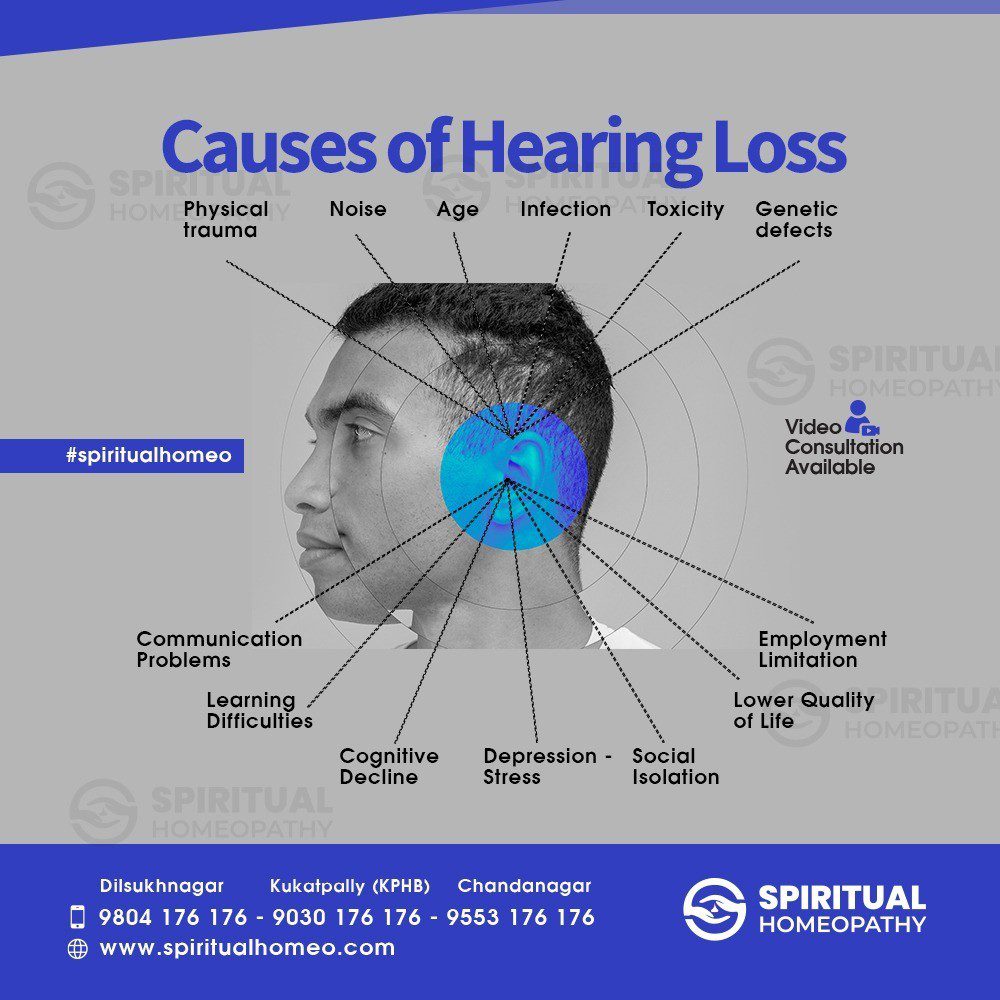
Hearing loss can have various causes, and it can occur at different stages of life. The causes of hearing loss can be broadly classified into two categories: conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss.
Conductive Hearing Loss: Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is an issue with the transmission of sound waves through the outer or middle ear. Common causes of conductive hearing loss include:
-
Earwax blockage: Accumulation of earwax can block the ear canal, leading to a temporary conductive hearing loss.
-
Ear infections: Infections such as otitis media (middle ear infection) or otitis externa (outer ear infection) can cause inflammation and fluid buildup, resulting in temporary conductive hearing loss.
-
Perforated eardrum: A hole or tear in the eardrum can disrupt sound conduction, causing conductive hearing loss until the eardrum heals.
-
Middle ear abnormalities: Structural abnormalities in the middle ear, such as malformation of the ossicles (tiny bones), can hinder sound transmission.
-
Tumors or growths: Benign tumors, can affect the movement of the middle ear structures, leading to conductive hearing loss.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when there is damage to the inner ear (cochlea) or the auditory nerve. It is the most common type of hearing loss and is often permanent. Causes of sensorineural hearing loss include:
-
Aging (Presbycusis): Age-related changes in the inner ear structures and nerve pathways can lead to gradual sensorineural hearing loss.
-
Noise exposure: Prolonged exposure to loud noises, such as machinery noise, music concerts, or explosions, can damage the delicate hair cells in the inner ear, causing sensorineural hearing loss.
-
Genetic factors: Certain genetic mutations or inherited conditions can predispose individuals to sensorineural hearing loss.
-
Ototoxic medications: Some medications, such as certain antibiotics , high-dose aspirin, can damage the inner ear and result in hearing loss.
-
Viral or bacterial infections: Infections like meningitis, measles, mumps, or cytomegalovirus can cause sensorineural hearing loss, particularly if they occur during infancy or early childhood.
-
Head trauma: Severe head injury or skull fractures can damage the inner ear structures or the auditory nerve, leading to sensorineural hearing loss.
-
Meniere’s disease: A disorder characterized by recurring episodes of vertigo, tinnitus, and sensorineural hearing loss.
It is important to note that some individuals may have a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, known as mixed hearing loss. Additionally, certain medical conditions, medications, and lifestyle factors can contribute to hearing loss.
Specific homeopathic medications can help to control the symptoms and also to improve the patient condition.