Homeopathy treatment for Speech Delay
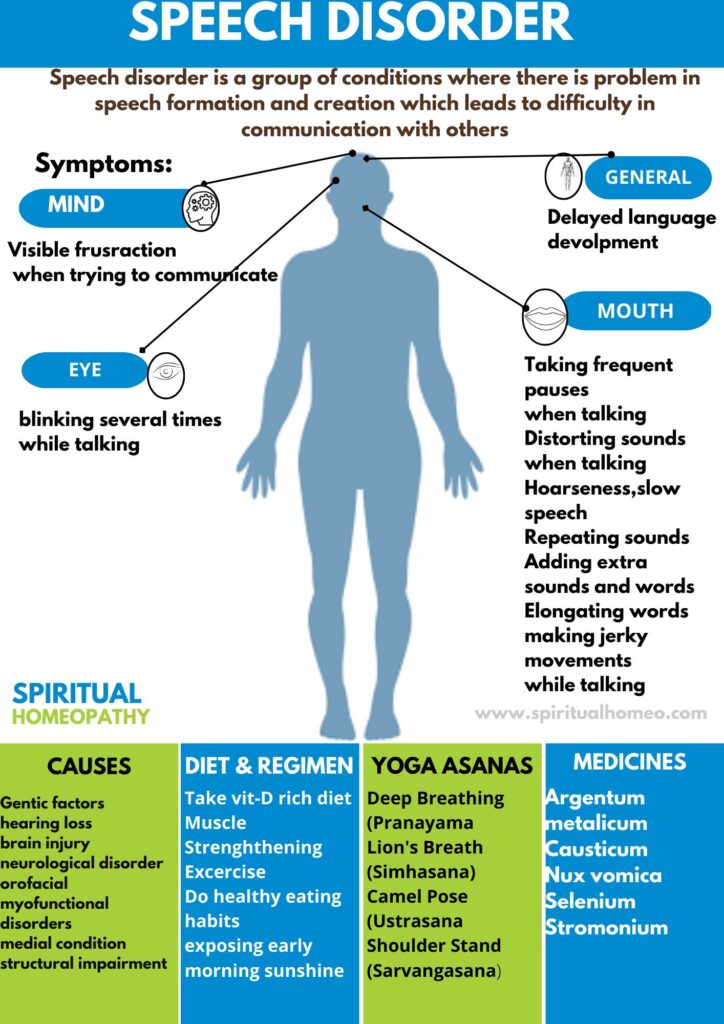
Speech disorder is a group of conditions where there is problem in speech formation and creation which leads to difficulty in communication with others.
- Overview
- Causes
- Types
- Sign & Symptoms
- What to eat
- Diet and Regiment
- Homeopathic Treatment
- FAQ
- Reference
In generally, Speech impairment mainly includes articulation, fluency and voice disorder problems.
Fluency is a part of proper speech. But in speech disorders there can be great disfluencies where there is repetition of words like in stuttering.
Either Stuttering or Stammering is the most common disfluency. Although it is common in young children, persistence of significant stammering even after 4 years of age is worrying.
Speech disorder can be because of articulation problems like denture misalignment, cleft palate, poor muscle coordination as either in cerebral palsy or in brain injury.
Speech is distorted here making it hard for listeners to understand in speech disorder.
Other speech Disorders
Voice disorders where there is obstruction in the airways like vocal cord tumors, enlarged adenoids etc.
Even things like voice overuse, screaming, singing, acid reflux moving up, nerve damage, vocal cord tumors etc can cause voice disorders.
Voice is hoarse, breaking, raspy, pitch and volume is altered, nasal tones etc are there in voice disorder.
Speech production also includes process like Phonation (a process, where voice produces as air in lung, moves up and vibrates the vocal cords) also Resonance (this air now passes through throat, nose and mouth).
Problems in Phonation and Resonance process leads to voice disorders. Furthermore, This includes altered voice quality, pitch, hyper or hypo nasal tone.
Speech disorders are not same as language disorders.
Speech disorders prevent people from forming correct speech sounds, while language disorders affect a person’s ability to learn words or understand what others say to them.
However, both speech and language disorders can make it more difficult for a person to express their thoughts and feelings to others.
Causes
Hearing loss:
Impaired hearing is a very common cause of Speech Disorders.
Heredity:
- Family heredity may be responsible for Speech Disorder
- Heredity may also determine size of child’s mouth, jaw; teeth arrangement; strength of facial muscles which plays a role in proper speech.
- Also there could be a strong family inheritance in stuttering. This is one of the important causes of speech disorders.
Neurological Disorder:
- Progressive neurological disorder can cause speech disorders.
- Conditions like brain tumour, traumatic brain injury, muscular dystrophy, autism, cerebral palsy,
Down syndrome, Parkinson’s disease and dementia etc may also cause speech disorder.
Orofacial myofunctional disorders:
This disorder causes speech disorder by exaggerated forward movement of tongue during speech or swallowing.
This is normal in infancy but improves as we grow up. But if it fails to improve it can lead to speech disorders. This is one of the chief causes of speech disorders.
Medical Condition:
- Enlarged adenoids or tonsils can also block the airways leading to forward protrusion of the tongue.
- Also damage to vocal cord, polyps, nodules, vocal cord paralysis, oral cancer, laryngeal carcinomas may cause Speech Disorders. These are leading causes of speech disorders.
Brain injury:
Stroke can result in apraxia of speech
Poor intellect:
It can also result in speech disorders.
Physical or structural impairment:
Structural impairments like cleft lips, cleft palate, tongue deformities, dental deformities can also cause speech disorders.
Types
Speech disorders can affect people of all ages.
Some types of speech disorder include stuttering, apraxia, and dysarthria & articulation problems.
1. Stuttering (Stammering):
Stuttering refers to a speech disorder that interrupts the flow of speech.
People who stutter can experience the following types of disruption i.e.:
- Repetitions occur when people involuntarily repeat sounds, vowels, or words.
- Blocks happen when people know what they want to say but have difficulty making the necessary speech sounds. Blocks may cause someone to feel as though their words are stuck.
- Prolongations refer to the stretching or drawing out of particular sounds or words.
The symptoms of stuttering can vary depending on the situation.
Stress, excitement, or frustration can cause stuttering to become more severe. Some people may also find that certain words or sounds can make a stutter more pronounced.
Stuttering can cause both behavioral and physical symptoms that occur at the same time.
These can include:
- Tension in the face and shoulders
- Rapid blinking
- Lip tremors
- Clenched fists
- Sudden head movements
There are two main types of stuttering:
- Developmental stuttering affects young children who are still learning speech and language skills. Genetic factors significantly increase a person’s likelihood of developing this type of stutter.
- Neurogenic stuttering occurs when damage to the brain prevents proper coordination between the different regions of the brain that play a role in speech.
2. Apraxia:
- The brain controls every single action that people make, including speaking. Most of the brain’s involvement in speech is unconscious and automatic.
- When someone decides to speak, the brain sends signals to the different structures of the body that work together to produce speech.
- The brain instructs these structures how and when to move to form the appropriate sounds.
- For example, these speech signals open or close the vocal cords, move the tongue and shape the lips, and control the movement of air through the throat and mouth.
- Apraxia is a general term referring to brain damage that impairs a person’s motor skills, and it can affect any part of the body.
- Apraxia of speech, or verbal apraxia, refers specifically to the impairment of motor skills that affect an individual’s ability to form the sounds of speech correctly, even when they know which words they want to say.
3. Dysarthria:
Dysarthria occurs when damage to the brain causes muscle weakness in a person’s face, lips, tongue, throat, or chest.
Muscle weakness in these parts of the body can make speaking very difficult.
People who have dysarthria may experience the following symptoms:
- Slurred speech
- Mumbling
- Speaking too slowly or too quickly
- Soft or quiet speech
- Difficulty moving the mouth or tongue
4. Sound speech disorders (articulation problems)
5. Speech disorder due to mutism
6. Voice disorders
Speech disorders can affect people of all ages.
Some types of speech disorder include stuttering, apraxia, and dysarthria & articulation problems.
1. Stuttering (Stammering):
Stuttering refers to a speech disorder that interrupts the flow of speech.
People who stutter can experience the following types of disruption i.e.:
- Repetitions occur when people involuntarily repeat sounds, vowels, or words.
- Blocks happen when people know what they want to say but have difficulty making the necessary speech sounds. Blocks may cause someone to feel as though their words are stuck.
- Prolongations refer to the stretching or drawing out of particular sounds or words.
The symptoms of stuttering can vary depending on the situation.
Stress, excitement, or frustration can cause stuttering to become more severe. Some people may also find that certain words or sounds can make a stutter more pronounced.
Stuttering can cause both behavioral and physical symptoms that occur at the same time.
These can include:
- Tension in the face and shoulders
- Rapid blinking
- Lip tremors
- Clenched fists
- Sudden head movements
There are two main types of stuttering:
- Developmental stuttering affects young children who are still learning speech and language skills. Genetic factors significantly increase a person’s likelihood of developing this type of stutter.
- Neurogenic stuttering occurs when damage to the brain prevents proper coordination between the different regions of the brain that play a role in speech.
2. Apraxia:
- The brain controls every single action that people make, including speaking. Most of the brain’s involvement in speech is unconscious and automatic.
- When someone decides to speak, the brain sends signals to the different structures of the body that work together to produce speech.
- The brain instructs these structures how and when to move to form the appropriate sounds.
- For example, these speech signals open or close the vocal cords, move the tongue and shape the lips, and control the movement of air through the throat and mouth.
- Apraxia is a general term referring to brain damage that impairs a person’s motor skills, and it can affect any part of the body.
- Apraxia of speech, or verbal apraxia, refers specifically to the impairment of motor skills that affect an individual’s ability to form the sounds of speech correctly, even when they know which words they want to say.
3. Dysarthria:
Dysarthria occurs when damage to the brain causes muscle weakness in a person’s face, lips, tongue, throat, or chest.
Muscle weakness in these parts of the body can make speaking very difficult.
People who have dysarthria may experience the following symptoms:
- Slurred speech
- Mumbling
- Speaking too slowly or too quickly
- Soft or quiet speech
- Difficulty moving the mouth or tongue
4. Sound speech disorders (articulation problems)
5. Speech disorder due to mutism
6. Voice disorders
Speech Sound Disorders
Inability to Pronounce Words Correctly: This may include difficulty pronouncing certain sounds or substituting sounds (e.g., saying “wabbit” instead of “rabbit”).
Omission of Sounds: Missing sounds in words (e.g., saying “ca” for “cat”).
Distorted Sounds: Sounds may be distorted, which makes speech unclear.
Difficulty Saying Complex Words: Struggling to say long words or multi-syllable words correctly.
2. Stuttering (Fluency Disorder)
Repetition of Sounds or Words: Repeating the first sound or syllable in words (e.g., “b-b-b-baby”).
Prolongation of Sounds: Stretching out a sound or syllable (e.g., “sssss-oon”).
Blocks: A pause or blockage in speech, where the speaker is unable to produce a sound for several seconds.
Tension and Struggle: Visible signs of tension, such as eye blinking, facial grimacing, or struggling to get words out.
Avoidance of Certain Words: Avoiding speaking certain words or situations because of fear of stuttering.
Speech Disruption Under Stress: The stutter may become more noticeable when the person is anxious, excited, or under pressure.
3. Apraxia of Speech (Motor Speech Disorder)
Difficulty Planning Speech Movements: A person may know what they want to say but have trouble coordinating the muscles needed for speech.
Inconsistent Errors: Speech errors can vary, even when trying to say the same word multiple times.
Mispronounced Words: Using incorrect sounds, syllables, or even whole words in place of what was intended.
Difficulty with Complex Sentences: Challenges with forming grammatically correct or more complex sentences.
Groping for Sounds: In some cases, the individual may seem to struggle with making the right sounds, with visible physical effort.
4. Dysarthria (Motor Speech Disorder)
Slurred Speech: Speech may sound slow, slurred, or unclear due to weakened speech muscles.
Soft or Muffled Voice: Difficulty controlling volume, resulting in a voice that may be too quiet or too loud.
Monotone Voice: A lack of variation in pitch or tone when speaking.
Inconsistent Speech Patterns: The person may have difficulty with rhythm, speed, or normal speech flow.
Difficulty with Breath Control: Problems with holding a breath while speaking or pausing appropriately.
Facial Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the muscles used for speech, such as drooping of the mouth or face.
5. Voice Disorders
Hoarseness: A raspy or rough voice that may sound strained or weak.
Voice Breaks: Sudden breaks or changes in pitch while speaking, which may be involuntary.
Lack of Volume: Speaking in a whisper or with a very soft voice that’s hard to hear.
Loss of Voice (Aphonia): Complete loss of voice, often due to vocal cord issues.
Breathy Voice: A breathy quality to the voice, which may make it sound like the person is struggling to speak.
6. Language Disorders (Affecting Speech and Understanding)
Difficulty Forming Sentences: Struggling to form grammatically correct sentences or convey complete thoughts.
Word-Finding Problems: Difficulty recalling specific words, often using fillers like “um” or “thing.”
Limited Vocabulary: Difficulty understanding or using a wide range of words.
Speech Delays: A noticeable delay in speech development (especially in children).
Difficulty Understanding Language: Struggling to follow directions, understand questions, or process spoken language.
Inappropriate Use of Words: Using the wrong word in a sentence (e.g., saying “dog” instead of “cat”).
7. Speech Disorders in Children
Delayed Speech Development: A child may not be speaking by the expected age or may have limited speech.
Limited Speech Output: Using a limited range of sounds or vocabulary compared to peers.
Difficulty with Pronunciation: Persistent mispronunciations of words, even as the child grows older.
Speech Regression: Losing previously learned speech skills after a period of development.
Difficulty with Social Communication: Challenges in using speech to engage in conversation or social settings.
8. Aphasia (Language Disorder from Brain Injury or Stroke)
Difficulty Speaking: Struggling to form words, sentences, or communicate thoughts clearly.
Difficulty Finding the Right Words: Using incorrect words or leaving words out of sentences.
Receptive Aphasia: Difficulty understanding spoken or written language.
Expressive Aphasia: Inability to speak or write clearly, even though the person may understand language well.
Foods to Eat for Speech Disorders
1. Foods to Support Brain Health
A healthy brain plays a key role in communication and speech. Certain nutrients can help improve cognitive function, memory, and the ability to process language.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These are important for brain health and may support cognitive function, memory, and focus.
Fatty Fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
Chia Seeds and Flaxseeds
Walnuts and Almonds
Avocados (also provide healthy fats)
Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Antioxidants help protect the brain from oxidative stress and inflammation, which can affect cognitive functions and speech.
Berries (blueberries, strawberries, blackberries)
Leafy Greens (spinach, kale, broccoli)
Nuts and Seeds (almonds, sunflower seeds)
B Vitamins: These vitamins, particularly B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are important for brain function, nerve health, and cognitive processing.
Whole Grains (brown rice, oats, quinoa)
Eggs (rich in B vitamins)
Leafy Greens (spinach, kale)
Legumes (lentils, chickpeas)
2. Foods to Support Muscle Health for Speech Production
The muscles involved in speech, including those of the mouth, tongue, and throat, need proper nutrition to function effectively. Foods rich in protein and certain vitamins can aid in muscle repair and strength.
Protein-Rich Foods: Protein helps repair and build muscle, which is important for speech articulation and movement.
Lean Meats (chicken, turkey)
Fish (salmon, tuna)
Eggs
Tofu and Tempeh
Legumes (lentils, beans)
Magnesium: This mineral helps with muscle function and can reduce muscle tension or spasms that may interfere with clear speech.
Leafy Greens (spinach, kale)
Nuts and Seeds (pumpkin seeds, almonds)
Whole Grains (quinoa, brown rice)
Bananas
Calcium: This mineral supports muscle function and nerve health.
Dairy Products (milk, yogurt, cheese)
Fortified Plant-Based Milks (almond, soy)
Leafy Greens (collard greens, spinach)
3. Foods for Hydration and Oral Health
Hydration and maintaining healthy oral tissues are important for clear speech production.
Water: Staying well-hydrated is crucial for maintaining the moisture in your mouth and throat, which helps prevent dryness and irritation.
Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially if you use your voice frequently.
Herbal Teas: Certain herbal teas can soothe the throat and improve hydration.
Chamomile Tea: Calms and soothes the throat.
Ginger Tea: Helps with throat inflammation and boosts circulation.
Licorice Root Tea: Traditionally used to soothe the throat and reduce irritation.
Coconut Water: Naturally hydrating and can help soothe dry throats.
4. Foods to Support Immune Health
Maintaining a strong immune system can help prevent infections that may affect the throat, vocal cords, and overall speech production.
Vitamin C-Rich Foods: Help strengthen the immune system and protect against throat infections.
Citrus Fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits)
Kiwi and Strawberries
Bell Peppers and Broccoli
Zinc-Rich Foods: Zinc is important for immune function and healing.
Pumpkin Seeds and Sunflower Seeds
Oysters and Lean Meats
Beans and Legumes
5. Foods to Reduce Inflammation
Inflammation in the body can affect the muscles used for speech and the overall function of the brain. Reducing inflammation can be helpful for improving speech clarity and muscle control.
Turmeric: Contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory compound that may support brain health and reduce inflammation in the body.
Add turmeric to soups, smoothies, or teas.
Ginger: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties and ability to soothe the digestive system and throat.
Fresh ginger tea, or adding ginger to dishes.
Olive Oil: Contains anti-inflammatory properties and healthy fats that support brain and muscle function.
Use extra virgin olive oil for cooking or as a salad dressing.
6. Foods to Avoid
Certain foods and drinks may irritate the throat or cause digestive discomfort, which can make speech harder. It’s best to avoid or limit:
Caffeine: Can lead to dehydration and irritation of the vocal cords.
Spicy Foods: May irritate the throat and make speaking uncomfortable.
Acidic Foods: Citrus fruits and tomatoes can exacerbate throat irritation in some people.
Dairy (for some people): Dairy can increase mucus production, which may make speaking more difficult.
Alcohol: Dehydrates the body and can irritate the throat and vocal cords.
Diet for Speech Disorders
1. Brain-Boosting Foods (Cognitive Support)
The brain plays a crucial role in speech and language processing. Nutrients that support brain health can enhance memory, focus, and cognitive processing, all of which are essential for effective speech.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Essential for brain function and development.
Fatty Fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
Chia Seeds, Flaxseeds
Walnuts
Avocados (rich in healthy fats)
Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Protects the brain from oxidative stress, enhancing cognitive abilities.
Berries (blueberries, strawberries, blackberries)
Leafy Greens (spinach, kale, broccoli)
Nuts (almonds, walnuts)
B Vitamins: Important for nerve function and overall brain health.
Whole Grains (brown rice, oats, quinoa)
Eggs
Leafy Greens (spinach, kale)
Legumes (lentils, beans)
2. Muscle-Strengthening Foods (For Speech Muscles)
The muscles involved in speech, including those in the mouth, throat, and tongue, need proper nutrition to function effectively. Eating foods that support muscle repair and strength can enhance speech production.
Protein-Rich Foods: Protein is essential for muscle growth and repair.
Lean Meats (chicken, turkey)
Fish (salmon, tuna)
Eggs
Legumes (lentils, chickpeas)
Tofu and Tempeh
Magnesium: Supports muscle relaxation and function.
Leafy Greens (spinach, kale)
Nuts and Seeds (pumpkin seeds, almonds)
Whole Grains (quinoa, brown rice)
Bananas
Calcium: Important for muscle contractions and nerve function.
Dairy Products (milk, yogurt, cheese)
Fortified Plant-Based Milks (almond, soy)
Leafy Greens (collard greens, spinach)
3. Hydration and Oral Health
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining the moisture of the mouth and throat, which aids in clear speech and vocal cord function.
Water: Hydration is key for speech production and vocal health.
Aim to drink 8-10 cups of water daily.
Herbal Teas:
Chamomile Tea: Soothes the throat and reduces inflammation.
Ginger Tea: Can improve circulation and soothe the throat.
Licorice Root Tea: Known to calm throat irritation and improve vocal health.
Coconut Water: A good alternative to plain water, it keeps you hydrated and can soothe the throat.
4. Foods for Immune Health
A strong immune system can help prevent infections that affect speech and the vocal cords. Incorporate immune-boosting foods to stay healthy and minimize throat issues.
Vitamin C-Rich Foods: Help fight infections and support throat health.
Citrus Fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits)
Kiwi and Strawberries
Bell Peppers and Broccoli
Zinc-Rich Foods: Important for immune function and healing.
Pumpkin Seeds and Sunflower Seeds
Lean Meats (chicken, turkey)
Beans (black beans, chickpeas)
5. Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Reducing inflammation can help improve the function of speech muscles and promote clearer speech. Inflammation in the throat or mouth can lead to discomfort and difficulty speaking.
Turmeric: Contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory compound.
Add turmeric to smoothies, soups, or teas.
Ginger: Another anti-inflammatory food that can reduce throat irritation.
Use fresh ginger in teas or recipes.
Olive Oil: Contains healthy fats and anti-inflammatory properties.
Use extra virgin olive oil for cooking or in salads.
Regimen for Speech Disorders
In addition to a healthy diet, establishing a daily regimen that includes good vocal practices, hydration, stress management, and consistent speech therapy is essential for managing speech disorders.
1. Regular Hydration
Drink Water: Keep hydrated throughout the day to maintain vocal cord moisture.
Avoid caffeine and alcohol, as they can dehydrate the body and irritate the throat.
2. Vocal Exercises
Regular vocal exercises can help strengthen the muscles used for speech and improve clarity and fluency.
Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing exercises can improve control over your breath, which is important for clear speech.
Practice diaphragmatic breathing by inhaling deeply through the nose and exhaling slowly through the mouth.
Pitch and Tone Control: Practice varying your pitch and tone to improve the quality and strength of your voice.
Try humming or singing simple melodies to improve vocal strength and control.
Articulation Practice: Regularly practice pronouncing difficult sounds or words, which can improve speech clarity.
Focus on precise articulation of sounds such as “r,” “s,” or “sh.”
3. Speech Therapy
Speech therapy is essential for addressing specific speech disorders, such as stuttering, apraxia, or dysarthria.
Work with a Speech Therapist: A licensed speech-language pathologist (SLP) can create a personalized plan for improving speech and communication skills.
Practice Daily: Consistent practice of speech exercises with a therapist or independently at home can help improve fluency, articulation, and overall speech ability.
4. Stress Management
Stress and anxiety can interfere with speech, especially in people who stutter or experience voice disorders. Managing stress can help improve communication.
Meditation: Practice mindfulness or guided meditation to reduce stress levels.
Relaxation Techniques: Progressive muscle relaxation and deep breathing exercises can help manage anxiety and tension.
Yoga: Yoga can improve overall well-being, reduce tension, and help with posture and breathing.
5. Avoiding Vocal Strain
Taking care of your voice is essential to avoid further strain or damage, especially if you’re dealing with a voice disorder.
Rest Your Voice: Avoid excessive talking or yelling. Take breaks to give your voice time to recover.
Avoid Throat Clearing: Throat clearing can irritate the vocal cords. Instead, try sipping water or swallowing gently.
6. Consistent Practice
Consistency is key in improving speech. Practice speaking slowly, clearly, and with good posture.
Daily Practice: Set aside time each day to practice speaking clearly and articulating words.
Use Technology: Consider using speech apps or audio recordings to practice pronunciation and fluency.
Why Choose Spiritual Homeopathy?
At Spiritual Homeopathy, we offer a unique approach to healing that integrates traditional homeopathic principles with a deep understanding of the spiritual aspects of health. Our team of experienced homeopathic practitioners combines expertise with empathy, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care tailored to your individual needs.
Our Approach to Treatment
We believe that true healing occurs when all aspects of a person—physical, emotional, and spiritual—are in balance. That’s why our treatment approach goes beyond simply addressing symptoms to identify and treat the underlying imbalances contributing to your health concerns. By addressing the root cause of illness and supporting your body’s innate healing ability, we empower you to achieve lasting health and vitality.
Services We Offer
Consultations: Our experienced best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad offer comprehensive consultations to assess your health concerns, medical history, and individual needs.we also take online consultation and We take the time to listen to your story, understand your unique health goals, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Remedies: At Spiritual Homeopathy, we provide a wide range of homeopathic remedies carefully selected to address a variety of health conditions. From acute ailments to chronic diseases, our remedies are safe, gentle, and effective, offering natural relief without the side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Follow-Up Care: We believe in the importance of ongoing support and monitoring throughout your healing journey. Our team is dedicated to providing regular follow-up care to track your progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that you are on the path to optimal health and well-being.
Our Commitment to You
At Spiritual Homeopathy, your health and wellness are our top priorities. We are committed to providing you with compassionate care, personalized treatment, and the support you need to achieve your health goals. Whether you are seeking relief from a specific health concern or simply looking to optimize your overall well-being, we are here to support you every step of the way.
What is Speech Disorder ?
Speech disorder is a group of conditions where there is problem in speech formation also creation which leads to difficulty in communication with others.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Speech Disorder ?
- Nux Vomica
- Stramonium
- Selenium
- Argentum Metallicum
What are the most common Speech Disorder ?
- Stuttering (Stammering)
- Apraxia
- Dysarthria
- Sound speech disorders
- Speech disorder due to mutism
- Voice disorders
What causes Speech Disorder ?
- Hearing loss
- Heredity
- Neurological Disorder
- Medical Condition
- Brain injury
- Poor intellect
- Orofacial myofunctional disorders
Give the symptoms of Speech Disorder ?
- Repeating sounds
- Adding extra sounds and words
- Elongating words
- Making jerky movements while talking
- Blinking several times while talking
- Visible frustration
- Taking frequent pauses
- Distorting sounds
- Delayed language development
- Slow speech
Reference
https://www.welcomecure.com/diseases/speech-disorders/homeopathic-treatment