Impulse Control Disorder
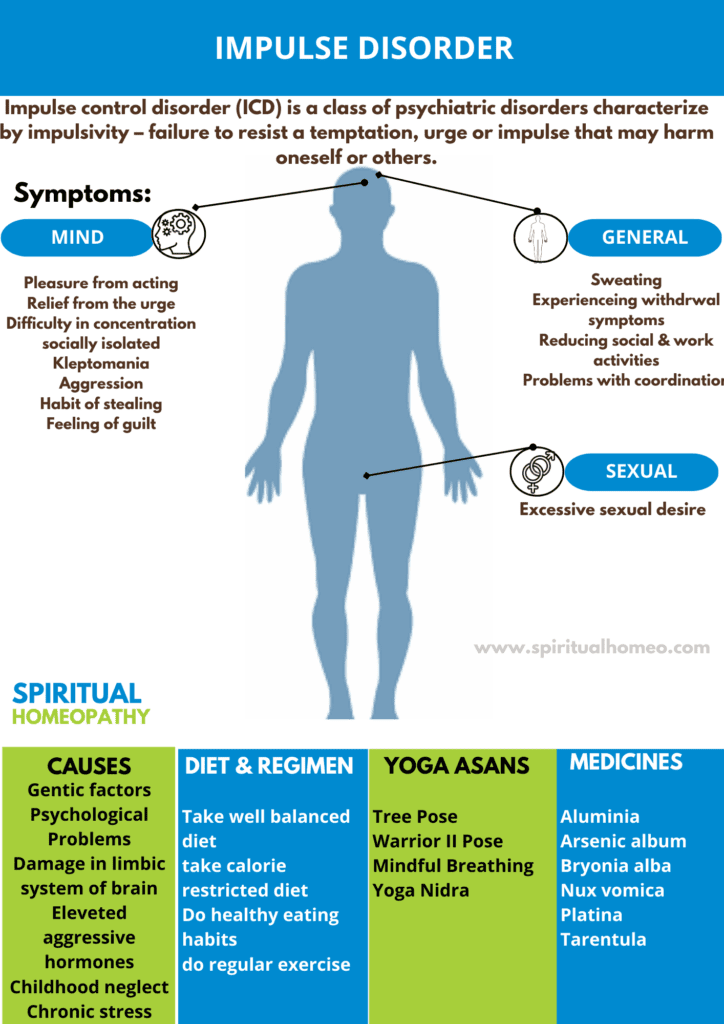
Impulse control disorder (ICD) is a class of psychiatric disorders characterize by impulsivity – failure to resist a temptation, urge or impulse that may harm oneself or others.
Many psychiatric disorders feature impulsivity, including substance-related disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, antisocial personality disorder, borderline personality disorder, conduct disorder and mood disorders.
Five behavioural stages can prove to be the symptoms of ICD:
- An impulse, growing tension, pleasure from acting, relief from the urge also finally guilt which may or may not arise.
- The signs and symptoms of impulse control disorders will vary based on the age of the children or adolescents suffering from them, the actual type of impulse control that they are struggling with, the environment in which they are living, and whether they are male or female.
- Disorders characterized by impulsivity that not categorised elsewhere in the DSM-IV-TR included in the category “Impulse control disorders not elsewhere classified”.
- Trichotillomania (hair-pulling) and skin-picking moved in DSM-5 to the obsessive-compulsive chapter.
- Additionally, other disorders not specifically listed in this category often classed as impulsivity disorders.
- Terminology hanged in the DSM-V from “Not Otherwise Classified” to “Not Elsewhere Classified”.
Sexual compulsion:
- Sexual compulsion includes an increased urge in sexual behavior and thoughts. Additionally, this compulsion may also lead to several consequences in the individual’s life.
- Including risky partner selection, increased chance for STD also depression.
- There has not yet been a determined estimate of its prevalence due to the secretiveness of the disorder.
Internet addiction:
- Basically, The disorder of Internet addiction has only recently take into consideration and has added as a form of ICD.
- It is characterize by excessive also damaging usage of Internet with increased amount of time spent chatting, web-surfing, gambling, shopping or exploring pornographic web-sites.
- Excessive and problematic Internet use has reported across all age, social, economical, also educational ranges.
- Although initially thought to occur mostly in males, increasing rates have also observed in females.
- However, no epidemiological study has conducted yet to understand its prevalence.
Compulsive shopping:
- Compulsive shopping or buying is characterize by a frequent irresistible urge to shop even if the purchases not needed or cannot affordable.
- Furthermore, The prevalence of compulsive buying in the U.S. is 2–% in the general adult population, with 80–90% of these cases being females.
- The onset believed to occur in late teens or early twenties also the disorder is believe to be generally chronic.
Pyromania:
- Pyromania is characterized by impulsive and repetitive urges to deliberately start fires. Because of its nature, the number of studies performed for fire-setting understandably very few.
- However studies done on children and adolescents suffering from pyromania have reported its prevalence between 2.4%-3.5% in the United States.
- It has also observed that the incidence of fire-setting is more common in juvenile and teenage boys than girls of the same age.
Intermittent explosive disorder:
- Intermittent explosive disorder or IED is a clinical condition of experiencing recurrent aggressive episodes that are out of proportion of any given stressor.
- Earlier studies reported a prevalence rate between 1%-2% in a clinical setting, however a study done by Coccaro and colleagues in 2004 had reported about 11.1% lifetime prevalence and 3.2% one month prevalence in a sample of a moderate number of individuals (n=253).
- Based on the study, Coccaro and colleagues estimated the prevalence of IED in 1.4 million individuals in the US and 10 million with lifetime IED.
Kleptomania:
-
Kleptomania is characterize by an impulsive urge to steal purely for the sake of gratification. In the U.S. the presence of kleptomania unknown but has estimated at 6 per 1000 individuals.
-
Kleptomania is also thought to the cause of 5% of annual shoplifting in the U.S. If true, 100,000 arrests are made in the U.S. annually due to kleptomaniac behavior.
What causes impulse control disorders?
- Scientists don’t know what causes these disorders. But many things probably play a role, including physical or biological, psychological or emotional and cultural or societal factors.
- Scientists do suspect that certain brain structures-including the limbic system, linked to emotions and memory functions, and the frontal lobe, the part of the brain’s cortex linked to planning functions and controlling impulses-affect the disorder.
- Hormones associated with violence and aggression, such as testosterone, also could play a role in the disorders.
- For example, researchers or doctors have suggested that women might predispose to less aggressive types of impulse control disorders such as kleptomania or trichotillomania, and men might predispose to more violent and aggressive types such as pyromania and intermittent explosive disorder.
What is Impulse Control Disorder?
Impulse control disorder (ICD) is a class of psychiatric disorders characterize by impulsivity – failure to resist a temptation, urge or impulse that may harm oneself or others.
What are the types of Impulse Control Disorder?
- Sexual compulsion
- Internet addiction
- Compulsive shopping
- Pyromania
-
Kleptomania
- Intermittent explosive disorder
What causes Impulse Control Disorder?
- Physical or biological factors
- Psychological or emotional factors
- Cultural or societal factors
- Emotions and memory functions
- Hormones associated with violence and aggression (testosterone)
Give the symptoms of Impulse Control Disorder?
- Growing tension
- Pleasure from acting
- Relief from the urge
- Finally guilt which may or may not arise.