Homeopathy treatment for Functional Enuresis
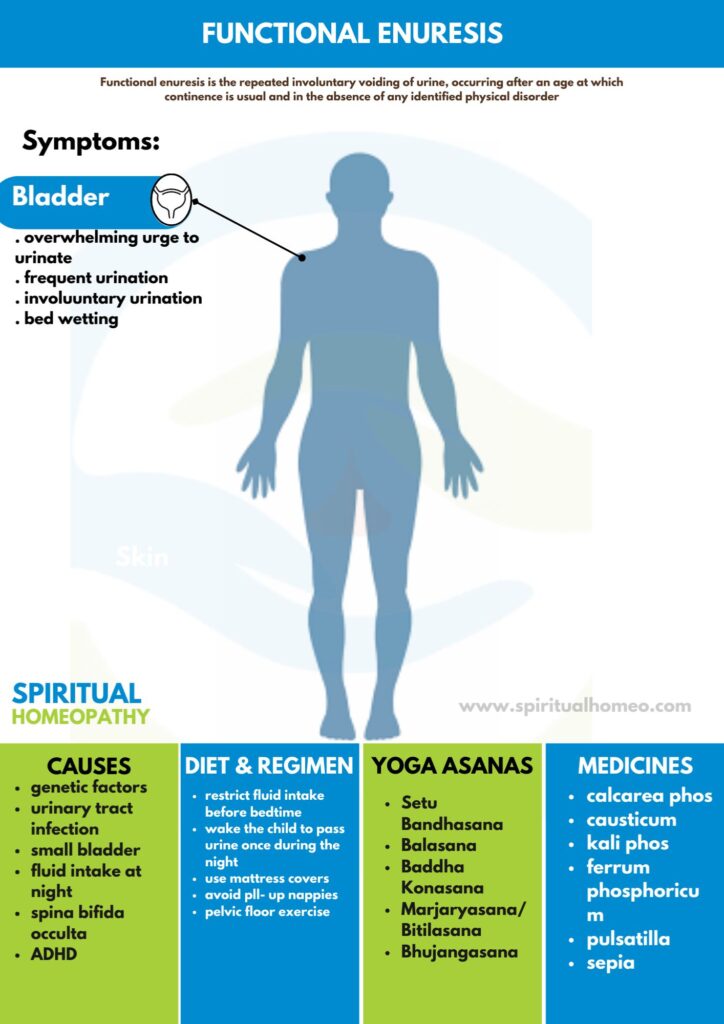
Functional Enuresis is the repeated involuntary voiding of urine, occurring after an age at which continence is usual and in the absence of any identified physical disorder.
- Overview
- Causes
- Types
- Sign & Symptoms
- What to eat
- Diet and Regiment
- Homeopathic Treatment
- FAQ
- Reference
OVERVIEW
The condition may be nocturnal (bed-wetting), diurnal (occurring during waking hours), or both.
Nocturnal enuresis is referred to as primary if there has been no preceding period of urinary continence, and secondary if there has been a preceding period of urinary continence.
There is no absolute period of continence needed to become secondary enuresis, but 6 months is a commonly used time frame.
Most children achieve regular daytime and night-time continence by 3 or 4 years of age, and 5 years is generally taken as the youngest age for the diagnosis.
Nocturnal enuresis can cause great unhappiness and distress, particularly if the parents blame or punish the child, and if the condition restricts staying with friends or going on holiday.
Nocturnal enuresis occurs in about;
- 10 % of children at 5 years of age,
- 4 % at 8 years,
- 1 % at 14 years,
- 0.5 % in adulthood.
The condition is more frequent in boys.
Daytime enuresis has a lower prevalence and is more frequent in girls.
CAUSES
The majority of cases of nocturnal primary enuresis are idiopathic; there is simply a delay in maturation of the nervous system controlling the bladder.
These children often have a family history of enuresis, as children who have either one or two parents who were enuretic have a 44 and 70 % chance, respectively, of being enuretic themselves.
There are a range of other causes of enuresis, but these are more commonly associated with secondary nocturnal or diurnal enuresis.
Common causes of nocturnal primary enuresis:
- Idiopathic developmental delay
- Genetics
Less common causes of enuresis (consider in secondary nocturnal or diurnal cases):
- Diabetes mellitus
- Abnormalities of the urinary tract (e.g. small bladder, vesicoureteric reflux)
- Structural abnormalities of the nervous system (e.g. spina bifida occulta)
- Chronic constipation
- Diuretics: e.g. caffeine, alcohol
ADHD
- Learning disorders or syndromes of developmental delay
- Behavioural: being too engaged in play or ‘leaving it too late’
- Psychological: i.e. a response to bereavement, stress, abuse, or bullying
- Obstructive sleep apnoea
- Epilepsy
Other Causes:
- Fluid intake at night.
- The bladder is irritated by the bowels.
- Inability to know if the bladder is filled.
- Urinary tract infection.
- Stress also anxiety.
- Hyperactivity in children.
- Lack of attention.
TYPES
Functional enuresis, or bedwetting, can be categorized into two main types:
Primary Enuresis: This type refers to children who have never achieved consistent nighttime dryness. It’s common in younger children and often resolves with age, though it can persist in some cases.
Secondary Enuresis: This occurs when a child who has previously been dry at night starts wetting the bed again after a period of dryness. It may be triggered by stress, trauma, urinary tract infections, or other medical conditions.
Both types can be influenced by genetic, environmental, or physiological factors. Treatment often involves behavioral strategies, bladder training, and sometimes medications. Consulting a healthcare professional is recommended for a proper diagnosis.
The symptoms of bladder dysfunction include:
1. Urge incontinence:
In detail, The presence of an overwhelming urge to urinate, frequent urination, attempts to hold the urine and urinary tract infections.
2. Voiding postponement:
Delaying urination in certain situations such as school.
3. Stress incontinence:
Generally, Incontinence that occurs in situations when increased intra-abdominal pressure occurs such as coughing.
4. Giggling incontinence:
Basically, Incontinence that occurs when laughing.
Secondary incontinence usually occurs in the context of a new life event that is stressful such as abuse or parental divorce.
WHAT TO EAT
For managing functional enuresis (bedwetting), a diet that supports bladder health and prevents irritation is important. Here’s a point-wise guide:
Hydrate Properly: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain hydration, but limit fluids 1-2 hours before bedtime.
Fiber-Rich Foods: Include fruits (like apples, pears), vegetables (like broccoli, carrots), and whole grains to prevent constipation, which can worsen enuresis.
Avoid Caffeine: Limit caffeinated drinks (like soda, coffee, tea) as they can irritate the bladder and increase urination.
Reduce Sugary & Acidic Foods: Limit sugary snacks, citrus fruits, and acidic foods that may irritate the bladder.
Magnesium-Rich Foods: Foods like leafy greens, nuts, and seeds may support muscle relaxation and bladder control.
Consult a healthcare provider for tailored dietary recommendations.
DIET AND REGIMEN
For managing functional enuresis (bedwetting), a balanced diet and regimen can help improve bladder control. Here’s a point-wise guide:
Increase Fluid Intake: Drink plenty of water during the day but reduce fluids 1-2 hours before bedtime to prevent nighttime accidents.
Avoid Caffeine and Sugary Drinks: Limit sodas, chocolate, and caffeinated beverages, as they can irritate the bladder.
Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support overall health.
Bladder Training: Gradually increase the time between bathroom visits to build bladder capacity.
Regular Bathroom Routine: Encourage frequent daytime bathroom trips every 2-3 hours, even if not feeling the urge.
Avoid Constipation: Include fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to prevent constipation, which can worsen enuresis.
Consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment.
Why Choose Spiritual Homeopathy?
At Spiritual Homeopathy, we offer a unique approach to healing that integrates traditional homeopathic principles with a deep understanding of the spiritual aspects of health. Our team of experienced homeopathic practitioners combines expertise with empathy, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care tailored to your individual needs.
Our Approach to Treatment
We believe that true healing occurs when all aspects of a person—physical, emotional, and spiritual—are in balance. That’s why our treatment approach goes beyond simply addressing symptoms to identify and treat the underlying imbalances contributing to your health concerns. By addressing the root cause of illness and supporting your body’s innate healing ability, we empower you to achieve lasting health and vitality.
Services We Offer
Consultations: Our experienced best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad offer comprehensive consultations to assess your health concerns, medical history, and individual needs. we also take online consultation and We take the time to listen to your story, understand your unique health goals, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Remedies: At Spiritual Homeopathy, we provide a wide range of homeopathic remedies carefully selected to address a variety of health conditions. From acute ailments to chronic diseases, our remedies are safe, gentle, and effective, offering natural relief without the side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Follow-Up Care: We believe in the importance of ongoing support and monitoring throughout your healing journey. Our team is dedicated to providing regular follow-up care to track your progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that you are on the path to optimal health and well-being.
Our Commitment to You
At Spiritual Homeopathy, your health and wellness are our top priorities. We are committed to providing you with compassionate care, personalized treatment, and the support you need to achieve your health goals. Whether you are seeking relief from a specific health concern or simply looking to optimize your overall well-being, we are here to support you every step of the way
FAQ
What is Functional Enuresis ?
Functional Enuresis is the repeated involuntary voiding of urine, occurring after an age at which continence is usual and in the absence of any identified physical disorder.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Functional Enuresis ?
- Calcarea phos
- Pulsatilla
- Ferrum phos
- Kali phos
- Sepia
What causes Functional Enuresis ?
- Idiopathic developmental delay
- Genetics
- Urinary tract infection
- Diabetes mellitus
- Abnormalities of the urinary tract
- Structural abnormalities of the nervous system
- Chronic constipation
- Diuretics: e.g. caffeine, alcohol
ADHD
What are the symptoms of Functional Enuresis ?
- Urge incontinence
- Voiding postponement
- Stress incontinence
- Giggling incontinence
REFFERNCE
Psychiatry, Fourth Edition – Oxford Medical Publications -SRG-by John Geddes, Jonathan Price, Rebecca McKnight / Ch 32.