Ebola virus
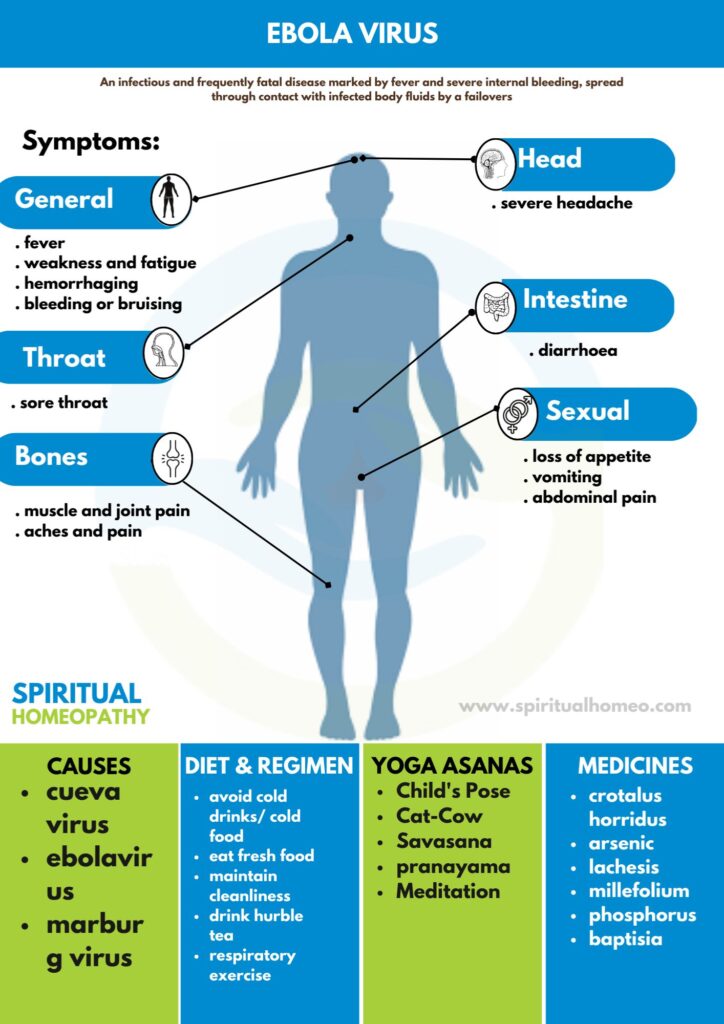
An infectious and frequently fatal disease marked by fever and severe internal bleeding, spread through contact with infected body fluids by a failover (Ebola virus), whose normal host species is unknown.
- Overview
- Causes
- Types
- Sign & Symptoms
- What to eat
- Diet and Regiment
- Homeopathic Treatment
- FAQ
- Reference
OVERVIEW
- In general, Several viruses of the family Filoviridae cause severe and frequently fatal viral hemorrhagic fevers in humans.
- Moreover, Introduction of filoviruses into human populations is an extremely rare event that most likely occurs by either direct or indirect contact with healthy mammalian filovirus hosts or by contact with infected, sick, or deceased nonhuman primates.
CAUSES
The family Filoviridae includes three genera: Cueva virus, Ebolavirus, also Marburg virus
These genomes contain six or seven genes that encode the following seven structural proteins:
nucleoprotein, polymerase cofactor (i.e. VP35), matrix protein (i.e. VP40), glycoprotein (e.g. GP1,2), transcriptional cofactor (VP30), secondary matrix protein (VP24), and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (L protein).
TYPES
Zaïre Ebolavirus
- Among the five strains, Zaïre Ebolavirus carries the highest mortality rate.
- A virus of the genus Ebolavirus is considered member of the species Zaire ebolavirus if:
- It is found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Gabon, or the Republic of the Congo.
- It has a genome with two or three gene overlaps (VP35/VP40, GP/VP30, VP24/L).
- It has a genomic sequence that differs from the virus type by less than 30%.
Sudan Ebolavirus
- A virus of the genus Ebolavirus is considered member of the species Sudan ebolavirus if:
- It is endemic in Sudan and/or Uganda.
- It has a genome with three gene overlaps (VP35/VP40, GP/VP30, VP24/L).
- It has a genomic sequence different from Ebola virus by ≥30%, but different from that of Sudan virus by <30%.
Reston Ebolavirus
- A virus of the genus Ebolavirus is considered member of the species Reston ebolavirus if:
- If its genome diverges from that of the prototype Reston virus, the Reston virus variant Pennsylvania, by ≤10% at the nucleotide level.
Tai (Ivory Coast) Ebolavirus
- A virus of the genus Ebolavirus is considered member of the species Tai Forest ebolavirus if:
- It is endemic in Côte d’Ivoire.
- It has a genome with three gene overlaps (VP35/VP40, GP/VP30, VP24/L).
- It has a genomic sequence different from Ebola virus by ≥30% but different from that of Tai Forest virus by <30%.
Bundibugyo Ebolavirus
- A virus of the genus Ebolavirus is considered member of the species Bundibugyo ebolavirus if:
- It is endemic in Uganda.
- It has a genome with three gene overlaps (VP35/VP40, GP/VP30, VP24/L).
- It has a genomic sequence different from Ebola virus by ≥30%, but different from that of Bundibugyo virus by <30%.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Fever
- Aches and pains, e.g. severe headache and muscle and joint pain
- Weakness also fatigue
- Sore throat
- Loss of appetite
- Gastrointestinal symptoms including abdominal pain, diarrhea, also vomiting
- Unexplained either haemorrhaging, bleeding or bruising
What to Eat for Ebola Virus Recovery
Hydrating Foods – Coconut water, soups, and electrolyte-rich fluids prevent dehydration from vomiting and diarrhea.
High-Protein Foods – Eggs, chicken, fish, and legumes help repair tissues and boost immunity.
Vitamin C-Rich Foods – Oranges, lemons, bell peppers, and strawberries strengthen the immune system.
Iron-Rich Foods – Spinach, red meat, and lentils help combat anemia caused by blood loss.
Zinc-Rich Foods – Nuts, seeds, and shellfish support wound healing and immunity.
Healthy Fats – Avocados, olive oil, and nuts provide energy and reduce inflammation.
Easily Digestible Foods – Rice, bananas, applesauce, and toast are gentle on the stomach.
Probiotic Foods – Yogurt and fermented foods support gut health.
Avoid Processed & Sugary Foods – These weaken immunity and cause inflammation.
DIET AND REGIMEN
- Avoid cold drinks /cold food
- Eat fresh food
- Maintain cleanliness
- Drink Hurble tea
- Respiratory exercise
Why Choose Spiritual Homeopathy?
At Spiritual Homeopathy, we offer a unique approach to healing that integrates traditional homeopathic principles with a deep understanding of the spiritual aspects of health. Our team of experienced homeopathic practitioners combines expertise with empathy, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care tailored to your individual needs.
Our Approach to Treatment
We believe that true healing occurs when all aspects of a person—physical, emotional, and spiritual—are in balance. That’s why our treatment approach goes beyond simply addressing symptoms to identify and treat the underlying imbalances contributing to your health concerns. By addressing the root cause of illness and supporting your body’s innate healing ability, we empower you to achieve lasting health and vitality.
Services We Offer
Consultations: Our experienced best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad offer comprehensive consultations to assess your health concerns, medical history, and individual needs. we also take online consultation and We take the time to listen to your story, understand your unique health goals, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Remedies: At Spiritual Homeopathy, we provide a wide range of homeopathic remedies carefully selected to address a variety of health conditions. From acute ailments to chronic diseases, our remedies are safe, gentle, and effective, offering natural relief without the side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Follow-Up Care: We believe in the importance of ongoing support and monitoring throughout your healing journey. Our team is dedicated to providing regular follow-up care to track your progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that you are on the path to optimal health and well-being.
Our Commitment to You
At Spiritual Homeopathy, your health and wellness are our top priorities. We are committed to providing you with compassionate care, personalized treatment, and the support you need to achieve your health goals. Whether you are seeking relief from a specific health concern or simply looking to optimize your overall well-being, we are here to support you every step of the way.
FAQ
What is Ebola virus?
An infectious and frequently fatal disease marked by fever and severe internal bleeding, spread through contact with infected body fluids by a failover (Ebola virus), whose normal host species is unknown.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Ebola virus?
- Crotalus horridus
- Arsenicum album
- Lachesis
- Millefolium
- Baptisia
What causes Ebola virus?
Cueva virus, Ebolavirus, and Marburg virus
What are the symptoms of Ebola virus
Fever
- Aches also pains
- Weakness and fatigue
- Sore throat
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain, diarrhea, also vomiting
- Unexplained hemorrhaging, bleeding or bruising
REFFERNCE
- Harrison-s_Principles_of_Internal_Medicine-_19th_Edition-_2_Volume_Set
- Materia Medica By Boericke W.
- Ebola risk factors – wikidoc