Dysentery
Dysentery refers to the presence of grossly visible blood in the stools and is a consequence of infection of the colon and Liver by either bacteria or ameba.
- Overview
- Causes
- Types
- Sign & Symptoms
- What to eat
- Diet and Regiment
- Homeopathic Treatment
- FAQ
- Reference
OVERVIEW
Bacillary dysentery is much more common in children than amebic dysentery.
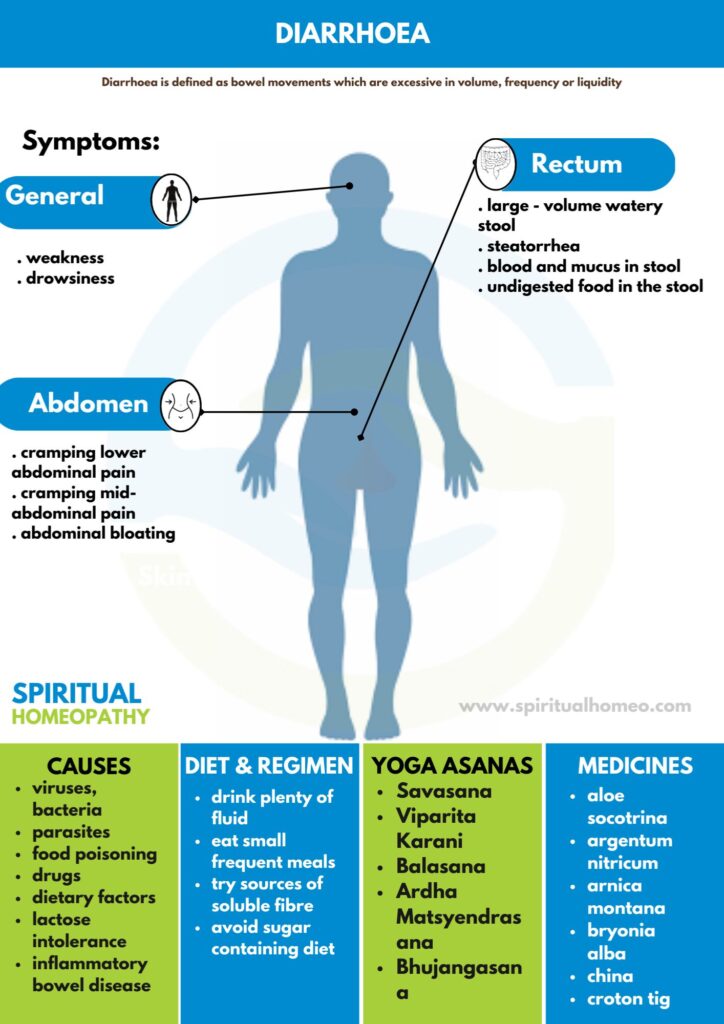
CAUSES
Major Causes of Dysentery:
Bacterial Dysentery:
- Shigella: The most common cause of bacterial dysentery. Shigella dysenteriae is particularly virulent.
- Salmonella: Some strains can cause dysentery, although they more commonly cause enterocolitis.
- Campylobacter jejuni: Often acquired from contaminated food or water.
- Escherichia coli (E. coli): Certain strains, such as Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC), can cause dysentery-like symptoms.
Parasitic Dysentery:
- Entamoeba histolytica: The protozoan parasite responsible for amoebic dysentery. It invades the colon wall and causes ulcers.
Viral Dysentery:
- Rotavirus and norovirus: These viruses typically cause gastroenteritis but can sometimes lead to symptoms resembling dysentery, especially in young children.
TYPES
The people experiencing dysentery either develop amoebic dysentery and bacterial dysentery.
- Bacterial
- Dysentery or Bacillary Dysentery
- This type of dysentery is a result of infection with bacteria from Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, or enterohemorrhagic E. coli.
- The diarrhea from Shigella is also called shigellosis. Shigellosis happens to be the most common type of dysentery.
2. Amoebic
Dysentery
- Also known as amoebiasis, amoebic dysentery is caused by a single-celled parasite infecting the intestines.
- This type of dysentery is a rare occurrence in the developed world and is mostly found in the tropical locales with poor sanitation.
- A person can also become infected if he or she traveled to a country where it is an endemic.
Signs and Symptoms of Dysentery:
- Frequent, loose, or watery stools.
- Presence of blood and mucus in the stools.
Abdominal Pain and Cramping:
- Severe, colicky abdominal pain.
- Cramping that may be relieved by passing stools.
Fever:
- Moderate to high fever, often accompanying the onset of symptoms.
Nausea and Vomiting:
- Nausea may occur with or without vomiting.
Tenesmus:
- A sensation of needing to pass stools even when the bowels are empty.
- Painful straining during bowel movements.
Dehydration:
- Symptoms of dehydration due to excessive fluid loss, including dry mouth, decreased urine output, and dizziness.
- Severe dehydration can lead to shock, which is a medical emergency.
WHAT TO EAT
Here’s what to eat for dysentery, described point-wise:
Clear Liquids: Drink water, oral rehydration solutions (ORS), or clear broths to replace lost fluids and electrolytes.
BRAT Diet: Eat bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast. These bland, low-fiber foods help soothe the gut and firm up stools.
Boiled Potatoes: Plain boiled potatoes without butter or seasoning can provide energy without irritating the digestive system.
Plain Crackers: Opt for plain, unsalted crackers, which are easy to digest and gentle on the stomach.
Cooked Carrots: Soft, well-cooked carrots provide soluble fiber to help firm stools.
Probiotic Foods: Include plain yogurt or kefir with probiotics to promote gut health and restore good bacteria.
Avoid Dairy: Limit dairy products, as they can worsen symptoms.
Avoid Fatty/Spicy Foods: Steer clear of greasy, fried, or spicy foods that can irritate the intestines.
Hydrate Frequently: Drink small amounts of fluids regularly to prevent dehydration.
Small, Frequent Meals: Eat small portions throughout the day to reduce stress on the digestive system.
DIET AND REGIMEN
- Avoid dairy products. If you have lactose intolerance, then dairy products can be a major cause of diarrhoea and should be avoided in general.
- Do steer clear of too much fiber. Fiber is incredibly healthy when it comes to your everyday diet.
- Eat a simple diet. The traditional anti-diarrhoea diet was the “BRAT” diet, which stood for bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast.
- Wash your hands regularly. When you do wash, scrub your palms, the back of your hands, between your fingers, and under your nails, and do it for at least 20 seconds
- Stay hydrated. Above most other things, replenishing the fluids that can be lost during severe diarrhoea is an important step to take.
Why Choose Spiritual Homeopathy?
At Spiritual Homeopathy, we offer a unique approach to healing that integrates traditional homeopathic principles with a deep understanding of the spiritual aspects of health. Our team of experienced homeopathic practitioners combines expertise with empathy, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care tailored to your individual needs.
Our Approach to Treatment
We believe that true healing occurs when all aspects of a person—physical, emotional, and spiritual—are in balance. That’s why our treatment approach goes beyond simply addressing symptoms to identify and treat the underlying imbalances contributing to your health concerns. By addressing the root cause of illness and supporting your body’s innate healing ability, we empower you to achieve lasting health and vitality.
Services We Offer
Consultations: Our experienced best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad offer comprehensive consultations to assess your health concerns, medical history, and individual needs. we also take online consultation and We take the time to listen to your story, understand your unique health goals, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Remedies: At Spiritual Homeopathy, we provide a wide range of homeopathic remedies carefully selected to address a variety of health conditions. From acute ailments to chronic diseases, our remedies are safe, gentle, and effective, offering natural relief without the side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Follow-Up Care: We believe in the importance of ongoing support and monitoring throughout your healing journey. Our team is dedicated to providing regular follow-up care to track your progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that you are on the path to optimal health and well-being.
Our Commitment to You
At Spiritual Homeopathy, your health and wellness are our top priorities. We are committed to providing you with compassionate care, personalized treatment, and the support you need to achieve your health goals. Whether you are seeking relief from a specific health concern or simply looking to optimize your overall well-being, we are here to support you every step of the way.
FAQ
What is Dysentery
Dysentery refers to the presence of grossly visible blood in the stools and is a consequence of infection of the colon and Liver by either bacteria or ameba.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Dysentery
- Aloe
- Arsenic Alb
- Baptisia
- Carbo Veg
- Cinchona
- Colchicum
- Colocynth
- Dioscorea
- Kali bich
- Nux Vomica
- Sulphur
What are the symptoms of Dysentery
Fever and diarrhea
- Diarrhea- watery, mucus and blood mixed with stools
- Tenesmus
- Dehydration
- Dyselectrolytemia
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome
- Convulsions
What causes Dysentery
- Shigella species
- Enteroinvasive
- Enterohemorrhagic E. coli
- Salmonella
- Campylobacter jejuni
- Medications – Rifaximin, Sulfasalazine
- Cancer
Paediatrics 8th Edition – O.P. Ghai
REFFERNCE
- https://www.lybrate.com/topic/diet-for-dysentery
- Therapeutic Pointers To Some Common Diseases By E.A. Farrington.
- https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Dysentery_physical_examination
Dysentery Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment (hlives.com)
Dysentery: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment (clevelandclinic.org)