Constipation
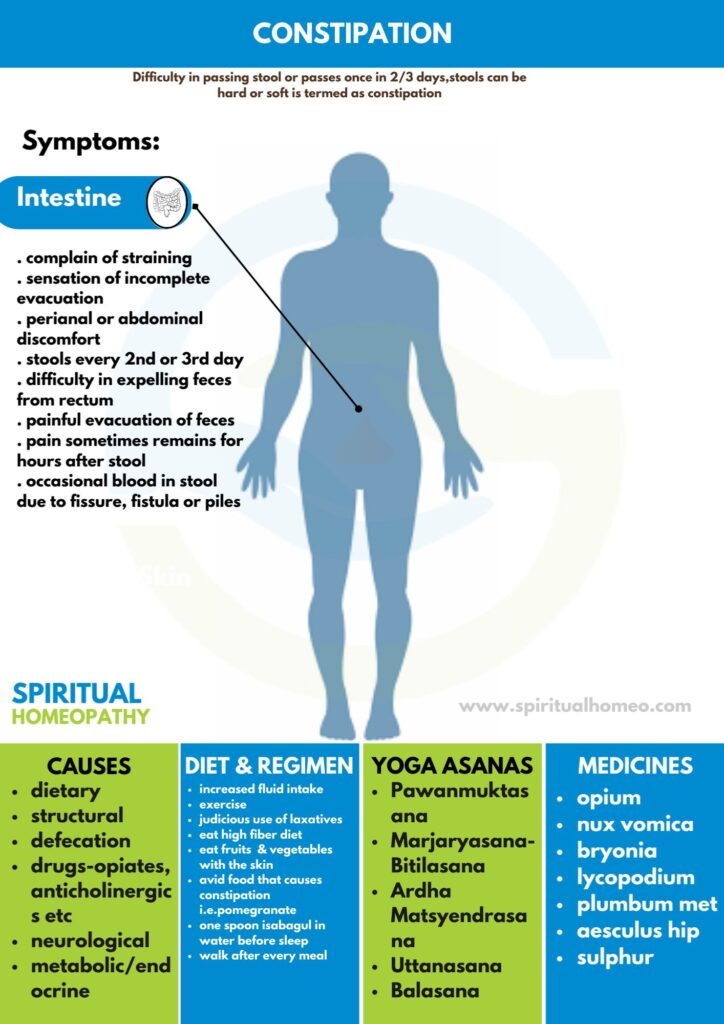
Difficulty in passing stool or passes once in 2 / 3 days, stools can be hard or soft is termed as constipation. which is also defined as infrequent passage of hard stool. Even ineffectual urge or a sensation of incomplete stools can be termed as constipation.
- Overview
- Causes
- Types
- Sign & Symptoms
- What to eat
- Diet and Regiment
- Homeopathic Treatment
- FAQ
- Reference
OVER VIEW
It may occur in many gastrointestinal and other medical disorders.
Demography
According to northern Indian community study, 555/4767 (11.6%) reported symptoms ofconstipation. Likewise in the former group, 1404 (53%) had self-perceived constipation. And in the latter, 846 (18%), 1030 (23%) reported straining at stools, and incomplete stool evacuation, respectively. Similarly in another community survey in rural northern India, the prevalence ofconstipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-C) was 2.4%.
Two smaller community surveys from Chandigarh and Bangalore reported the prevalence ofconstipation of 24.8% and 8.6%, respectively. Though the latter study was conducted exclusively among elderly population, in an eastern Indian study, of 331 consecutive patients with ChronicConstipation. In which 65% were older than 60 years.
CAUSES
1. Gastrointestinal disorders
Dietary i.e.
- Lack of fibers also fluid intake Motility
- Slow-transit of constipation
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Drugs (see below)
- Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction
Structural i.e.
- Colonic carcinoma
- Diverticular disease
- Hirschsprung’s disease
Defecation i.e.
- Anorectal disease (e.g. Crohn’s, fissures, hemorrhoids)
- Obstructed defecation
2. Non-gastrointestinal disorders
Drugs i.e.
- Opiates
- Anticholinergics
- Calcium antagonists
- Iron supplements
- Aluminum-containing antacids
Neurological i.e.
- Multiple sclerosis
- Spinal cord lesions
- Cerebrovascular accidents
- Parkinsonism
Metabolic/endocrine i.e.
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypercalcemia
- Hypothyroidism
- Pregnancy
Others
- Any serious illness with immobility, especially in the elderly
TYPES
Obstructive constipation: is the result of actual physical obstruction of the passage of feces. Causes include cystic fibrosis (in children), tumors, adhesions, scars formed in the abdomen (mostly after abdominal surgery), strictures firmed within the intestine (mostly caused by inflammation, like in Crohn’s disease), or damaged pelvic nerves (injuries, neurological diseases) that prevent relaxation of anal muscles.
- Atonic constipation: is the result of lack of intestinal muscle tone (tension) of the colon, abdominal wall or pelvic floor, also known as lazy colon. Person with this kind simply does not feel the urge to defecate even when the colon is full of feces. It may occur in elderly or bedridden patients or after prolonged dependence on laxatives. Most common among old people (weak muscle tone), woman (pelvic floor weakness), and diabetics (damage to intestinal nerves).
- Spastic constipation: is result from colonic spasms caused by irritation of the bowel or intestines. In this case, a diet that is low in fiber is usually suitable. It is also a symptom of irritable bowel syndrome.
Based on the duration they are of two types
- Acute constipation (occasional problem) – constipation occurs suddenly and last for few days. Acute constipation with worrisome symptoms such as rectal bleeding, abdominal pain and cramps, nausea and vomiting, and involuntary loss of weight needs urgent diagnosis.
- Chronic constipation (persistent problem) – is the constipation that lasts for longer durations. Your need medication and lifestyle change to normalize bowel movement.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
- Complain of straining
- Moreover, Sensation of incomplete evacuation
- Either perianal or abdominal discomfort
- Stools every 2nd or 3rd day
- Additionally, Difficulty in expelling faeces from rectum
- Painful evacuation of faeces
- Besides this, Pain sometimes remains for hours after passing stool
- Lastly, Occasional blood in stool due to fissure, either fistula or piles
WHAT TO EAT
For managing constipation, a high-fiber, hydration-rich diet can help promote regular bowel movements. Here’s a point-wise breakdown:
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Eat whole grains (oats, brown rice), beans, lentils, and vegetables like broccoli, carrots, and spinach to add bulk to stool.
- Fruits: Apples, pears, berries, and prunes are high in fiber and can help soften stool.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water and herbal teas (like peppermint or ginger) to keep stool hydrated and easier to pass.
- Healthy Fats: Include olive oil, avocado, and flaxseeds to lubricate the digestive tract.
- Probiotics: Yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods promote gut health and regularity.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, and sunflower seeds provide fiber and healthy fats.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Limit refined foods and dairy, which may exacerbate constipation.
Consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist.
DIET AND REGIMEN
Increased fluid intake
- Exercise
- Judicious use of laxatives.
- Eat high fibre diet – whole grains, bran, oat, green leafy vegetables, peas, beans, potatoes, raw vegetables, salads, dried fruits also fresh fruits
- Eat fruits also vegetables with the skin
- Avoid food that can cause constipation like pomegranate etc
- You can take one spoon Isabagul (e.g. fibre, Psyllium) in water before retiring to bed
- Walk after every meal
Why Choose Spiritual Homeopathy?
At Spiritual Homeopathy, we offer a unique approach to healing that integrates traditional homeopathic principles with a deep understanding of the spiritual aspects of health. Our team of experienced homeopathic practitioners combines expertise with empathy, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care tailored to your individual needs.
Our Approach to Treatment
We believe that true healing occurs when all aspects of a person—physical, emotional, and spiritual—are in balance. That’s why our treatment approach goes beyond simply addressing symptoms to identify and treat the underlying imbalances contributing to your health concerns. By addressing the root cause of illness and supporting your body’s innate healing ability, we empower you to achieve lasting health and vitality.
Services We Offer
Consultations: Our experienced best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad offer comprehensive consultations to assess your health concerns, medical history, and individual needs. we also take online consultation and We take the time to listen to your story, understand your unique health goals, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Remedies: At Spiritual Homeopathy, we provide a wide range of homeopathic remedies carefully selected to address a variety of health conditions. From acute ailments to chronic diseases, our remedies are safe, gentle, and effective, offering natural relief without the side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Follow-Up Care: We believe in the importance of ongoing support and monitoring throughout your healing journey. Our team is dedicated to providing regular follow-up care to track your progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that you are on the path to optimal health and well-being.
Our Commitment to You
At Spiritual Homeopathy, your health and wellness are our top priorities. We are committed to providing you with compassionate care, personalized treatment, and the support you need to achieve your health goals. Whether you are seeking relief from a specific health concern or simply looking to optimize your overall well-being, we are here to support you every step of the way.
FAQ
What is Constipation
Difficulty in passing stool or passes once in 2 / 3 days, stools can be hard or soft is termed as constipation.
Constipation is also defined as infrequent passage of hard stool.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Constipation
- Opium
- Nux vomica
- Pulsatilla
- Bryonia
- Lycopodium
- Plumbum met
- Aesculus
What are the symptoms of Constipation?
- Complain of straining
- Sensation of incomplete evacuation
- Either perianal or abdominal discomfort
- Stools every 2nd or 3rd day
- Difficulty in expelling faeces from rectum
- Painful evacuation of faeces
- Pain- remains for hours after passing stool
- Occasional blood
Causes
- Lack of fibers and fluid intake
- Slow-transit constipation
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction
- Anorectal disease
- Obstructed defecation
- Opiates, Calcium antagonists, Iron supplements
- Diabetes mellitus, Hypothyroidism
- Pregnancy
- Any serious illness with immobility
REFFERENCE
- Davidson’s Principles and Practice of Medicine (22nd edition)
- Hompath Zomeo Ultimate lane software/Diet and nutrition
Constipation physical examination – wikidoc