Homeopathy treatment for Celiac Disease
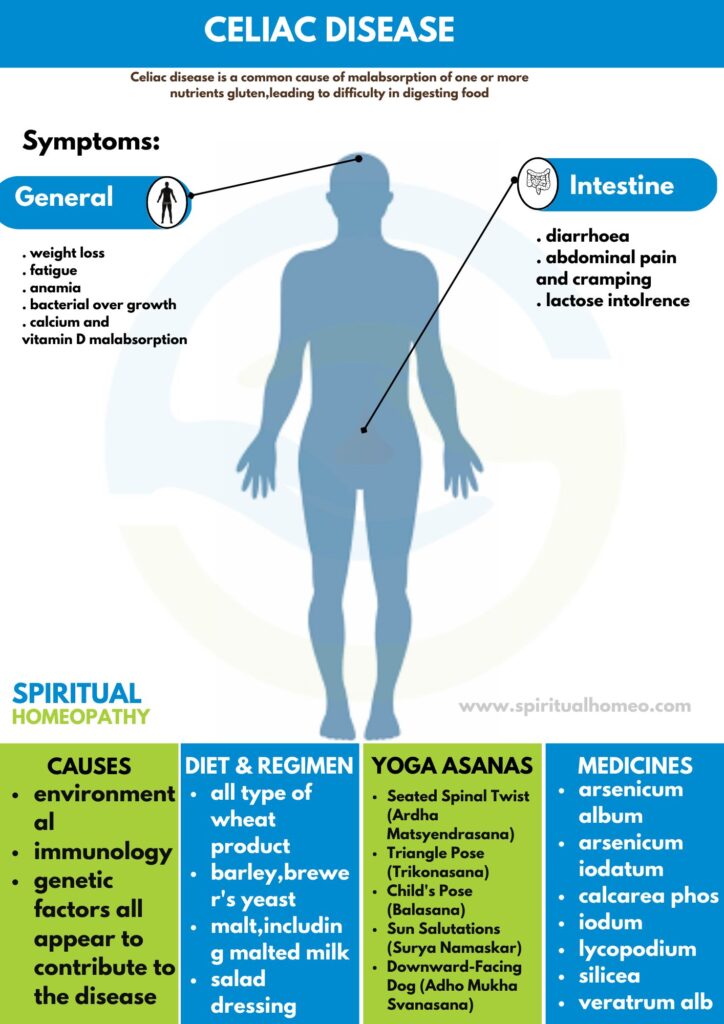
Celiac disease is a common cause of malabsorption of one or more nutrients. Additionally, a disease in which the small intestine is hypersensitive to gluten, leading to difficulty in digesting food.
- Overview
- Causes
- Types
- Sign & Symptoms
- What to eat
- Diet and Regiment
- Homeopathic Treatment
- FAQ
- Reference
OVERVIEW
In general, celiac disease was originally considered largely a disease of white individuals, especially persons of European descent.
Comparatively, Its incidence has increased over the past 50 years. Moreover, Celiac disease has had several other names, including nontropical sprue, celiac sprue, adult celiac disease, also gluten-sensitive enteropathy.
CAUSES
The etiology of celiac disease is not known but following factors are mainly involved in this condition:
- Environmental i.e.:
- One environmental factor is the clear association of the disease with gliadin, a component of gluten that is present in wheat, barley, also rye.
- Immunologic i.e.:
- Critical also involves both adaptive and innate immune responses.
- Immunological factors
- Genetic factors
- Auto immune disease
TYPES
1. Classical celiac disease:
Patients have signs and symptoms i.e.:
- Malabsorption
- Diarrhea
- Steatorrhea (especially; pale, foul-smelling, fatty stools)
- Weight loss
- Growth failure in children.
2. Non-classical celiac disease:
- Mild gastrointestinal symptoms
- Abdominal distension also pain
- Iron-deficiency anemia
- Chronic fatigue
- Chronic
migraine
- Peripheral neuropathy (tingling, either numbness or pain in hands or feet)
- Vitamin deficiency (e.g. folic acid and B12)
- Silent celiac disease:
- It is also known as asymptomatic celiac disease.
- Patients do not complain of any symptoms, but still experience villous atrophy damage to their small intestine.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Patient of celiac disease is either asymptomatic or having symptoms for example,
- Malabsorption of multiple nutrients
- Steatorrhea
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Nausea also Vomiting
- Bloating also Gas
- Abdominal Pain
WHAT TO EAT
For celiac disease, a strict gluten-free diet is essential to manage symptoms and prevent damage to the intestines. Here’s a guide:
- Gluten-Free Grains: Choose rice, quinoa, oats (labeled gluten-free), corn, and gluten-free pasta as safe carb sources.
- Lean Proteins: Include chicken, fish, eggs, tofu, and legumes for muscle repair and immune support.
- Fruits & Vegetables: Eat a variety of fresh fruits and vegetables like berries, leafy greens, and carrots to provide essential vitamins and fiber.
- Healthy Fats: Include avocado, olive oil, and nuts to promote heart and brain health.
- Dairy: Opt for gluten-free dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt unless lactose intolerant.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Avoid foods with hidden gluten, such as processed snacks, sauces, or packaged meals. Always check labels.
DIET AND REGIMEN
Here are the foods with gluten celiac patients should avoid i.e.:
- Wheat including spelt
- Farro
- Graham
- Khorasan wheat
- Semolina
- Durum
- Wheatberries
- Rye
- Barley
- Triticale
- Malt
- Brewer’s yeast
- Wheat starch
- Beer
- Bread
- Desserts, like cake, cookies, and pie
- Cereal
- Crackers and seasoned potato chips
- French fries
- Pasta
- Processed meat, including hot dogs and lunch meat
- Salad dressing
- Sauces
- Soups
You also want to consider other more hidden sources of gluten, i.e.:
- Medication
- Vitamins also supplements
- Lipstick and lip balm
- Communion wafers
- Eggs at restaurants
- Play dough that you may handle before giving to your children
- Toothpaste also mouthwash
HOMEOPATHIC TREATMENT
Why Choose Spiritual Homeopathy?
At Spiritual Homeopathy, we offer a unique approach to healing that integrates traditional homeopathic principles with a deep understanding of the spiritual aspects of health. Our team of experienced homeopathic practitioners combines expertise with empathy, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care tailored to your individual needs.
Our Approach to Treatment
We believe that true healing occurs when all aspects of a person—physical, emotional, and spiritual—are in balance. That’s why our treatment approach goes beyond simply addressing symptoms to identify and treat the underlying imbalances contributing to your health concerns. By addressing the root cause of illness and supporting your body’s innate healing ability, we empower you to achieve lasting health and vitality.
Services We Offer
Consultations: Our experienced best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad offer comprehensive consultations to assess your health concerns, medical history, and individual needs.we also take online consultation and We take the time to listen to your story, understand your unique health goals, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Remedies: At Spiritual Homeopathy, we provide a wide range of homeopathic remedies carefully selected to address a variety of health conditions. From acute ailments to chronic diseases, our remedies are safe, gentle, and effective, offering natural relief without the side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Follow-Up Care: We believe in the importance of ongoing support and monitoring throughout your healing journey. Our team is dedicated to providing regular follow-up care to track your progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that you are on the path to optimal health and well-being.
Our Commitment to You
At Spiritual Homeopathy, your health and wellness are our top priorities. We are committed to providing you with compassionate care, personalized treatment, and the support you need to achieve your health goals. Whether you are seeking relief from a specific health concern or simply looking to optimize your overall well-being, we are here to support you every step of the way.
FAQ
What is Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is a common cause of malabsorption of either one or more nutrients. A disease in which the small intestine is hypersensitive to gluten, leading to difficulty in digesting food
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Celiac Disease
- Antimonium Crudum
- Pulsatilla
- Arsenicum Album
- Lycopodium
- Iodum
- Podophyllum
- Natrum sulph
- China
- Carbo veg
What are the symptoms of Celiac Disease
- Malabsorption of multiple nutrients
Diarrhoea
- Steatorrhea
- Weight loss
Constipation
- Fatigue
- Nausea als Vomiting
- Bloating also Gas
- Abdominal Pain
Which Diet should be avoided in Celiac Disease
- Rye
- Wheat starch
- Beer, Bread
- Desserts, e.g. cake, cookies, also pie
- Cereal
- Seasoned potato chips
- French fries, Pasta
- Processed meat, including hot dogs also lunch meat
- Salad dressing
- Sauces, Soups
REFFERNCE
[1]Harrison-s_Principles_of_Internal_Medicine-_19th_Edition-_2_Volume_Set
[2] https://www.everydayhealth.com/celiac-disease/guide/diet/
[3] Homoeopathic Body-System Prescribing – A Practical Workbook of Sector Remedies
[4] https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/celiac-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20352220
[5] Textbook of medicine
[6] Materia Medica by Boericke W.
[7]https://www.google.com/search?q=celiac+disease+risk+factors&rlz
[8]https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Celiac_disease_physical_examination
[9]https://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/gi/celiac-disease/differential-diagnosis.html
[10]
[11]https://lompocvmc.com/blog/2060-what-causes-celiac-disease-an