Homeopathy treatment for Cataract
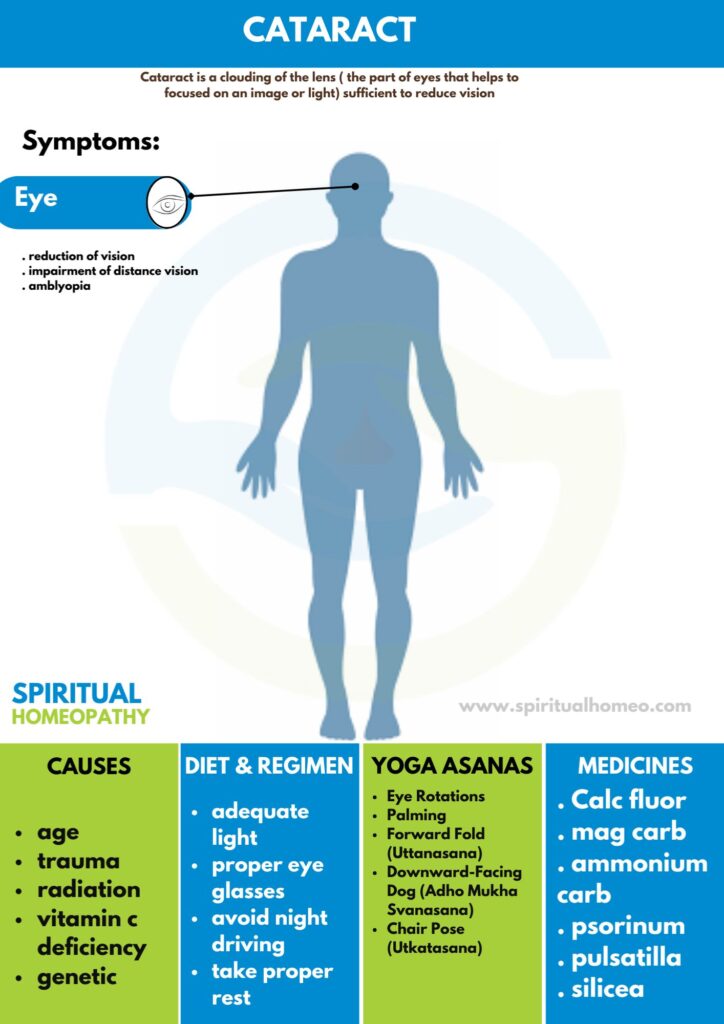
Cataract is a clouding of the lens (The part of eyes that Helps to focused on an image or light) sufficient to reduce vision.
- Overview
- Causes
- Types
- Sign & Symptoms
- What to eat
- Diet and Regiment
- Homeopathic Treatment
- FAQ
- Reference
OVERVIEW
Most cataracts develop slowly as a result of aging, leading to gradual impairment of vision.
CAUSES
Age
- Age is the most common cause. Lens proteins denature and degrade over time, and this process is accelerated by diseases such as diabetes mellitus and hypertension.
- Environmental factors, including toxins, radiation, and ultraviolet light have cumulative effects which are worsened by the loss of protective and restorative mechanisms due to alterations in gene expression and chemical processes within the eye.
Trauma
- Post traumatic rosette cataract of a 60-year-old male
- Blunt trauma causes swelling, thickening, and whitening of the lens fibers. While the swelling normally resolves with time, the white color may remain. In severe blunt trauma, or in injuries that penetrate the eye, the capsule in which the lens sits can be damaged.
- This damage allows fluid from other parts of the eye to rapidly enter the lens leading to swelling and then whitening, obstructing light from reaching the retina at the back of the eye.
- Cataracts may develop in 0.7 to 8.0% of cases following electric injuries, Blunt trauma can also result in star- (stellate) or petal-shaped cataracts.
Radiation
- Cataracts can arise as an effect of exposure to various types of radiation. X-rays, one form of ionizing radiation, may damage the DNA of lens cells.
- Ultraviolet light, specifically UVB, has also been shown to cause cataracts, and some evidence indicates sunglasses worn at an early age can slow its development in later life.
- Microwaves, a type of nonionizing radiation, may cause harm by denaturing protective enzymes (e.g., glutathione peroxidase), by oxidizing protein thiol groups (causing protein aggregation), or by damaging lens cells via thermoelastic expansion.
- The protein coagulation caused by electric and heat injuries whitens the lens.
- This same process is what makes the clear albumen of an egg become white and opaque during cooking.
Genetics
- Christmas tree cataract (Diffuse illumination)
- The genetic component is strong in the development of cataracts, most commonly through mechanisms that protect and maintain the lens.
- The presence of cataracts in childhood or early life can occasionally be due to a particular syndrome.
Skin diseases
- The skin and the lens have the same embryological origin and so can be affected by similar diseases.
- Those with atopic dermatitis and eczema occasionally develop shield ulcer cataracts.
- Ichthyosis is an autosomal recessive disorder associated with cuneiform cataracts and nuclear sclerosis.
- Basal-cell nevus and pemphigus have similar associations.
Smoking and alcohol
- Cigarette smoking has been shown to double the rate of nuclear sclerotic cataracts and triple the rate of posterior subcapsular cataracts.
Inadequate vitamin C
- Low vitamin C intake and serum levels have been associated with greater cataract rates.
Medications
- Some medications, for example systemic, topical, or inhaled corticosteroids, may increase the risk of cataract development.
- Corticosteroids most commonly cause posterior subcapsular cataracts.
- People with schizophrenia often have risk factors for lens opacities (e.g. diabetes, hypertension, and poor nutrition) but antipsychotic medications are unlikely to contribute to cataract formation.
- Miotics also triparanol may increase the risk.
Post-operative
- Nearly every person who undergoes a vitrectomy—without ever having had cataract surgery—will experience progression of nuclear sclerosis after the operation.
- This may because the native vitreous humour different from the solutions used to replace the vitreous (in other words, vitreous substitutes), such as BSS Plus.
- This may also because the native vitreous humors contains ascorbic acid which helps neutralize oxidative damage to the lens and because conventional vitreous substitutes do not contain ascorbic acid.
- Accordingly, for phasic patients requiring a vitrectomy it is becoming increasingly common for ophthalmologists to offer the vitrectomy combined with prophylactic cataract surgery to prevent cataract formation.
- The formation of cataract occurs more rapidly in patients with a history of ocular trauma, uveitis, or diabetes mellitu. Moreover, Trauma
- Radiation exposure, Radiation therapy also glucocorticoid treatment can induce cataract as a side effect. Additionally, The cataracts associated with either radiation or glucocorticoids have a typical posterior subcapsular location.
- Diabetes
- Besides this, Long standing use of Corticosteroids
- Lastly, Prolong used of alcohol, smoking tobacco
The main types of age-related cataracts are nuclear sclerosis, cortical, and posterior subcapsular.
Nuclear sclerosis:
- It is the most common type of cataract, and involves the central or ‘nuclear’ part of the lens.
- This eventually becomes hard, or ‘sclerotic’, due to condensation on the lens nucleus and the deposition of brown pigment within the lens.
- In its advanced stages it is called a brunescent cataract. In early stages, an increase in sclerosis may cause an increase in refractive index of the lens.
- This causes a myopic shift (lenticular shift) that decreases hyperopia and enables presbyopia patients to see at near without reading glasses.
- This is only temporary and is called second sight.
Cortical cataract:
- It is due to the lens cortex (outer layer) becoming opaque. They occur when changes in the fluid contained in the periphery of the lens causes fissuring.
- When these cataracts are viewed through an ophthalmoscope, or other magnification system, the appearance is similar to white spokes of a wheel.
- Symptoms often include problems with glare and light scatter at night.
Posterior subcapsular cataracts:
- It is cloudy at the back of the lens adjacent to the capsule (or bag) in which the lens sits. Because light becomes more focused toward the back of the lens, they can cause disproportionate symptoms for their size.
An immature cataract:
- It has some transparent protein, but with a mature cataract, all the lens protein is opaque.
- In a hypermature or Morgagnian cataract, the lens proteins have become liquid.
Congenital cataract:
- Which may be detected in adulthood, has a different classification and includes lamellar, polar, and sutural cataracts.
Cataracts can be classified by using the lens opacities classification system LOCS III. In this system, cataracts are classified based on type as
- Nuclear
- Cortical
- Posterior
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
- People with nuclear sclerotic or brunescent cataracts often notice a reduction of vision.
- Nuclear cataracts typically cause greater impairment of distance vision than of near vision.
- Those with posterior subcapsular cataracts usually complain of glare as their major symptom.
- Other symptoms include frequent changes of glasses and colored halos due to hydration of lens.
- Congenital cataracts can result in amblyopia if not treated in a timely manner.
WHAT TO EAT
For cataracts, a diet rich in antioxidants and nutrients can support eye health and potentially slow progression.
- Vitamin C: Include citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruit), strawberries, and bell peppers to support collagen production and protect the lens from damage.
- Vitamin E: Consume nuts, seeds, and leafy greens like spinach and kale for their protective antioxidant properties.
- Beta-Carotene: Add carrots, sweet potatoes, and pumpkin, which are rich in beta-carotene that helps maintain healthy eyes.
- Lutein and Zeaxanthin: Eat dark leafy greens, corn, and eggs to support eye health and filter harmful light.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Include fatty fish (salmon, sardines) and flaxseeds to reduce inflammation and promote eye function.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to maintain healthy eye moisture and overall health.
DIET AND REGIMEN
For cataracts, a healthy diet and regimen can support eye health and may slow progression:
- Balanced Diet: Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables, focusing on those rich in antioxidants, like citrus, berries, and leafy greens.
- Vitamin C: Include foods like oranges, strawberries, and bell peppers to protect the lens from oxidative damage.
- Vitamin E: Consume nuts, seeds, and spinach for their eye-protecting antioxidant benefits.
- Beta-Carotene: Add carrots, sweet potatoes, and kale to maintain eye health.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Eat fatty fish (salmon, sardines) and flaxseeds to reduce inflammation.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep eyes hydrated.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in light physical activity to improve circulation and overall well-being.
HOMEOPATHIC TREATMENT
Why Choose Homeopathy?
Homeopathy offers natural and holistic healing, treating the root cause of ailments without side effects. It strengthens the body’s defense system, is gentle for all ages, and personalized to each individual’s needs. Choose homeopathy for safe, effective, and long-lasting health solutions.
Spiritual Homeopathy: Your Path to Natural Healing
At Spiritual Homeopathy, where we believe in the power of holistic healing and personalized care. Our mission is to provide compassionate and effective homeopathic treatment to help you achieve optimal health and well-being. With a focus on addressing the root cause of illness and promoting harmony between mind, body, and spirit, we are dedicated to guiding you on your journey towards vibrant health and vitality.
Why Choose Spiritual Homeopathy?
At Spiritual Homeopathy, we offer a unique approach to healing that integrates traditional homeopathic principles with a deep understanding of the spiritual aspects of health. Our team of experienced homeopathic practitioners combines expertise with empathy, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care tailored to your individual needs.
Our Approach to Treatment
We believe that true healing occurs when all aspects of a person—physical, emotional, and spiritual—are in balance. That’s why our treatment approach goes beyond simply addressing symptoms to identify and treat the underlying imbalances contributing to your health concerns. By addressing the root cause of illness and supporting your body’s innate healing ability, we empower you to achieve lasting health and vitality.
Services We Offer
Consultations: Our experienced best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad offer comprehensive consultations to assess your health concerns, medical history, and individual needs. we also take online consultation and We take the time to listen to your story, understand your unique health goals, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Remedies: At Spiritual Homeopathy, we provide a wide range of homeopathic remedies carefully selected to address a variety of health conditions. From acute ailments to chronic diseases, our remedies are safe, gentle, and effective, offering natural relief without the side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Follow-Up Care: We believe in the importance of ongoing support and monitoring throughout your healing journey. Our team is dedicated to providing regular follow-up care to track your progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that you are on the path to optimal health and well-being.
Our Commitment to You
At Spiritual Homeopathy, your health and wellness are our top priorities. We are committed to providing you with compassionate care, personalized treatment, and the support you need to achieve your health goals. Whether you are seeking relief from a specific health concern or simply looking to optimize your overall well-being, we are here to support you every step of the way.
FAQ
What isCataract
Cataract is a clouding of the lens (The part of eyes that Helps to focused on an image or light) sufficient to reduce vision.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Cataract
Calcarea Carb
- Calcarea Flour
- Causticum
- Natrum Mur
- Phosphorus
- Silicea
What are the symptoms of Cataract
- Brunescent cataracts- reduction of vision
- Nuclear cataracts- impairment of distance vision
- Posterior subcapsular cataracts- complain of glare
- Colored halos
- Congenital cataracts- amblyopia
Name of the surgeries for Cataract
- Phacoemulsification
- Extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE)
- Manual small incision cataract surgery (MSICS)
- Intracapsular cataract extraction (ICCE)
REFFERNCE
[1]Harrisons_Principles_of_Internal_Medicine-_19th_Edition-_2_Volume_Set
[2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cataract
[3] https://www.drhomeo.com/homeopathic-treatment/homeopathic-medicines-for-cataract/
[5]https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cataracts/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353795
[6]https://www.google.com/search?q=cataract+physical+examination+findings&newwindow
[7]https://www.google.com/search?q=investigation+of+cataract&newwindow
[8]https://www.google.com/search?q=differential+diagnosis+of+cataract&newwindow