Bulimia Nervosa
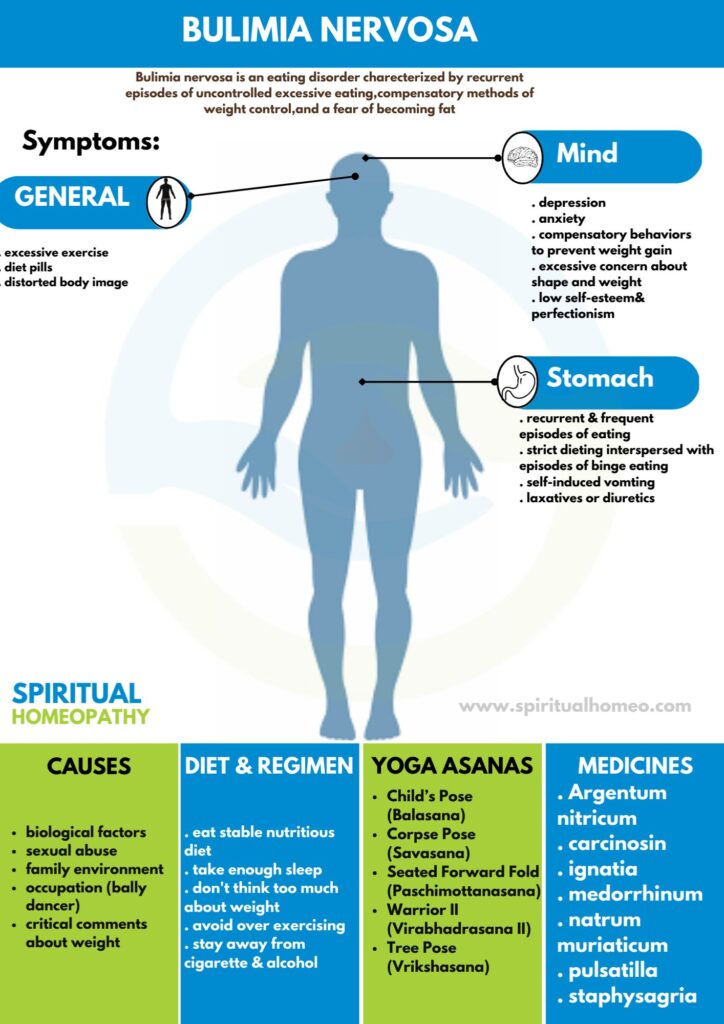
Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of uncontrolled excessive eating (in other words, ‘binges’), compensatory methods of weight control, and a fear of becoming fat.
- Overview
- Causes
- Types
- Sign & Symptoms
- What to eat
- Diet and Regiment
- Homeopathic Treatment
- FAQ
- Reference
OVERVIEW
The term bulimia refers only to the episodes of uncontrollable excessive eating, and may also be present in other forms of eating disorder.
Moreover, Unlike anorexia nervosa, for which there are historical accounts dating back to medieval times, bulimia nervosa was first described as a distinct clinical entity in 1979.
Gerald Russell, a British psychiatrist, published a case series of 30 patients with bulimia nervosa also used them to describe the defining features of the condition.
Since Russell’s initial work, it has been realized that bulimia nervosa is a common condition, additionally, effective treatments have since been developed to treat it.
CAUSES
Biological i.e.:
- Female sex Age (15–40 years)
- Family history of:
- Mood disorders
- Substance abuse
Eating disorder
Obesity
- Type 1 diabetes
- Early menarche
Psychological i.e.:
- Critical comments in early life about eating, either shape, or weight
- Family environment with a focus on shape also dieting
- either Sexual or physical abuse in childhood
- Low self-esteem
- Perfectionism
Social i.e.:
- Living in a developed country
- Cultures that encourage dieting and value thinness
- Occupation (e.g. ballet dancer)
TYPES
Bulimia of purging type
- This type is characterised by the use of self-induced vomiting or excessive usage of laxatives to purge food in order to prevent weight gain. Some patients may use diuretics.
2. Bulimia of non-purging type
- This type is characterised by using means, other than the self-induced methods, to avoid weight gain, like extreme degrees of fasting or excessive exercising that are both inappropriate.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
It is characterized by recurrent also frequent episodes of eating unusually large amounts of food also feeling a lack of control over these episodes.
This binge-eating is followed by behavior that compensates for the overeating for instance; forced vomiting, excessive use of laxatives or diuretics, fasting, excessive exercise, or a combination of these behaviors.
There is an intense fear of becoming higher-weight person . There may be an earlier history of anorexia nervosa.
It is usually body-image disturbance and the person is unable to perceive own body size accurately.
There is a persistent preoccupation with eating, also an irresistible craving for food. Besides this, There are episodes of overeating in which large amounts of food are consumed within short periods of time (eating binges).
Fascinated by food they sometimes buy magazines also cookbooks to read recipes, and enjoy discussing dieting issues.
Weight control e.g.:
- Strict dieting interspersed with episodes of indulging eating
- Compensatory behaviors to prevent weight gain
- Self-induced vomiting
- either Laxatives or diuretics
- Excessive exercise
- Diet pills
Psychopathology e.g.:
- Excessive concern about shape and weight
- Distorted body image
- Low self-esteem also perfectionism
Physical consequences of weight control behaviours i.e.:
- Normal body weight
- Hypokalaemia, hyponatremia, hypochloremia
- Menstrual abnormalities
- Swollen parotid glands
- Erosion of dental enamel
- Calluses of the dorsal aspect of the fingers (in other words, Russell’s sign)
- Peripheral oedemic
- Increased plasma amylase
Other comorbid psychiatric conditions e.g.:
Depression
- Anxiety
- Deliberate self-harm
- Misuse of either alcohol or drugs
- Borderline personality disorder
- serum electrolytes
- serum creatinine
- serum magnesium
- urine pregnancy test
- ECG
- serum ferritin
- serum B12
- serum red blood cell folate
WHAT TO EAT
For individuals with bulimia nervosa, a balanced diet and approach to eating can aid in recovery. Here’s a point-wise guide:
- Small, Balanced Meals: Eat 4–6 small meals throughout the day to regulate hunger and prevent binge eating.
- Protein: Include lean proteins (chicken, fish, tofu) to support muscle health and stabilize blood sugar.
- Complex Carbs: Incorporate whole grains like oats, quinoa, and brown rice for steady energy.
- Healthy Fats: Add sources of healthy fats like avocado, nuts, and olive oil to support brain and hormone function.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Focus on a variety of colorful produce (berries, leafy greens, carrots) for vitamins and antioxidants.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and aid digestion.
- Avoid Restriction: Focus on eating a wide variety of foods without severe restriction or guilt to promote a healthy relationship with food.
DIET AND REGIMEN
Eat stable nutritious diet.
- Take enough sleep.
- Don’t think too much about weight.
- Avoid over exercising.
- Stay away from cigarette & alcohol.
HOMEOPATHIC TREATMENT
Why Choose Spiritual Homeopathy?
At Spiritual Homeopathy, we offer a unique approach to healing that integrates traditional homeopathic principles with a deep understanding of the spiritual aspects of health. Our team of experienced homeopathic practitioners combines expertise with empathy, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care tailored to your individual needs.
Our Approach to Treatment
We believe that true healing occurs when all aspects of a person—physical, emotional, and spiritual—are in balance. That’s why our treatment approach goes beyond simply addressing symptoms to identify and treat the underlying imbalances contributing to your health concerns. By addressing the root cause of illness and supporting your body’s innate healing ability, we empower you to achieve lasting health and vitality.
Services We Offer
Consultations: Our experienced best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad offer comprehensive consultations to assess your health concerns, medical history, and individual needs. we also take online consultation and We take the time to listen to your story, understand your unique health goals, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Remedies: At Spiritual Homeopathy, we provide a wide range of homeopathic remedies carefully selected to address a variety of health conditions. From acute ailments to chronic diseases, our remedies are safe, gentle, and effective, offering natural relief without the side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Follow-Up Care: We believe in the importance of ongoing support and monitoring throughout your healing journey. Our team is dedicated to providing regular follow-up care to track your progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that you are on the path to optimal health and well-being.
Our Commitment to You
At Spiritual Homeopathy, your health and wellness are our top priorities. We are committed to providing you with compassionate care, personalized treatment, and the support you need to achieve your health goals. Whether you are seeking relief from a specific health concern or simply looking to optimize your overall well-being, we are here to support you every step of the way.
FAQ
What is Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of uncontrolled excessive eating (‘binges’), compensatory methods of weight control, and a fear of becoming fat.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Bulimia Nervosa
- Argentum nit
- Carcinosin
- Ignatia
- Medorrhinum
- Natrum mur
- Pulsatilla
- Staphysagria
What are the causes of Bulimia Nervosa
- Female sex Age (15–40 years)
- Family history
- Type 1 diabetes
- Early menarche
- Family environment with a focus on shape and dieting
- Sexual or physical abuse in childhood
- Low self-esteem
- Perfectionism
What are the symptoms of Bulimia Nervosa
- Strict dieting interspersed with episodes of indulging eating
- Compensatory behaviours to prevent weight gain
- Self-induced vomiting
- Laxatives or diuretics
- Excessive exercise, Diet pills
- Excessive concern about shape and weight
- Distorted body image
- Menstrual abnormalities
Depression, Anxiety
- Deliberate self-harm
REFFRENCE
- Psychiatry, Fourth Edition- Oxford Medical Publications – SRG- by Geddes, Jonathan Price, Rebecca McKnight / Ch 27.
- A Short Textbook of PSYCHIATRY 7th edition by Niraj Ahuja / ch 12.
- Homeopathy in treatment of Psychological Disorders by Shilpa Harwani / ch 15.
https://www.medainc.org/causes-and-risk-factors-for-bulimia-nervosa-2/
https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Bulimia_nervosa_pathophysiology
- https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-gb/441
- https://bulimiaguide.org/prevention-cure-triggers/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bulimia/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353621