Homeopathic treatment for Gall Bladder Stones
Gallstones (Cholelithiasis) is a small, hard crystalline mass formed abnormally in the gall bladder or bile ducts from bile pigments, cholesterol, also calcium salts. Gallstones can cause severe pain and blockage of the bile duct.
- Overview
- Causes
- Types
- Sign & Symptoms
- What to eat
- Diet and Regiment
- Homeopathic Treatment
- FAQ
- Reference
OVERVIEW
Generally, Gallstone formation is the most common disorder of the biliary tree and it is unusual for the gallbladder to be diseased in the absence of gallstones. Moreover, In developed countries, gallstones occur in 7% of males and 15% of females aged 18–65 years, with an overall prevalence of 11%. Individuals under 40 years there is a 3:1 female preponderance, whereas in the elderly the sex ratio is about equal.
In developed countries, the incidence of symptomatic gallstones appears to be increasing and they occur at an earlier age. Gallstones are less frequent in India, the Far East also Africa. There has been much debate over the role of diet in cholesterol gallstone disease; an increase in dietary cholesterol, fat, total calories and refined carbohydrate or lack of dietary fiber has been implicated. At present, the best data support an association between simple refined sugar in the diet and gallstones.
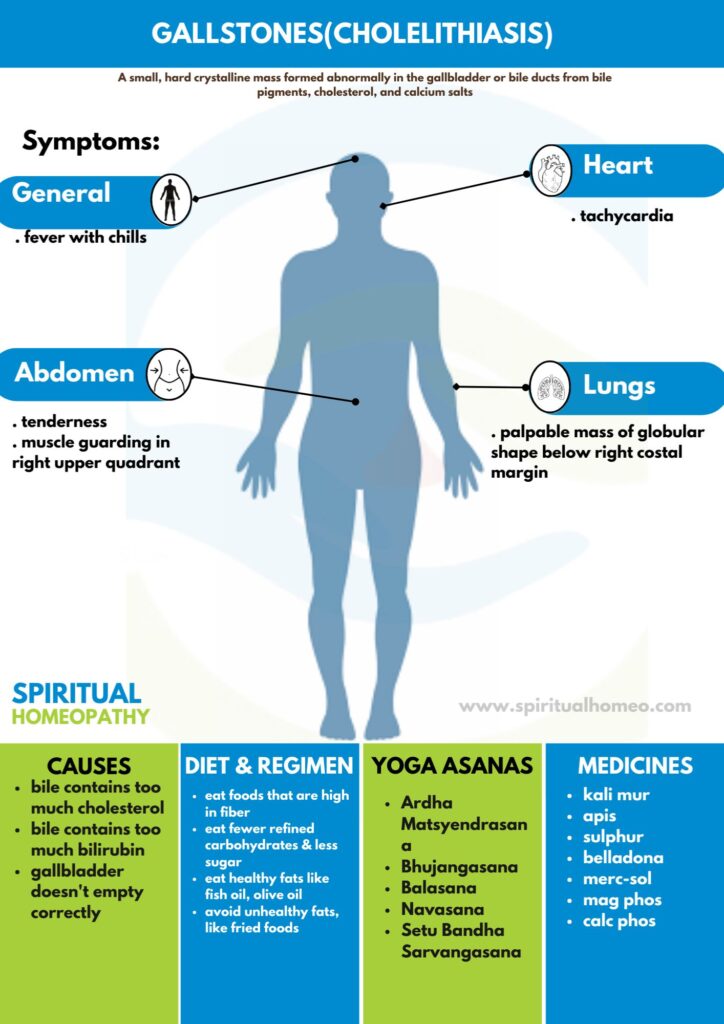
CAUSES
It’s not clear what causes gallstones to form. Doctors think gallstones may result when:
- Your bile contains too much cholesterol. Normally, your bile contains enough chemicals to dissolve the cholesterol excreted by your liver. But if your liver excretes more cholesterol than your bile can dissolve, the excess cholesterol may form into crystals and eventually into stones.
- Your bile contains too much bilirubin. Bilirubin is a chemical that’s produced when your body breaks down red blood cells. Certain conditions cause your liver to make too much bilirubin, including liver cirrhosis, biliary tract infections and certain blood disorders. The excess bilirubin contributes to gallstone formation.
Your gallbladder doesn’t empty correctly. If your gallbladder doesn’t empty completely or often enough, bile may become very concentrated, contributing to the formation of gallstones
Gallstones are conveniently classified into cholesterol or pigment stones, although the majority is of mixed composition. Cholesterol stones are most common in developed countries, whereas pigment stones are more frequent in developing countries. Gallstones contain varying quantities of calcium salts, including calcium bilirubinate, carbonate, phosphate also palmitate, which simper radio-opaque. All in all, Gallstone formation is multifactorial, toms are not now recognized as being caused by and the factors involved are related to the type of gallstone
TYPES
Types of gallstones that can form in the gallbladder include:
- Cholesterol gallstones. The most common type of gallstone, called a cholesterol gallstone, often appears yellow in colour. Additionally, these gallstones are composed mainly of undissolved cholesterol, but may contain other components.
- Pigment gallstones. These either dark brown or black stones form when your bile contains too much bilirubin.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
(I) General—Include fever with often chills at Onset, also tachycardia.
(II)Local—
(a) Tenderness and muscle guarding in right upper quadrant.
(b) Palpable mass of globular shape below right costal margin also moving on inspiration may be felt.
(c) Murphy’s sign – Patient complains of pain on taking a deep breath while the examiner’s hand is pressed below the right costal margin.
(d) Abdominal distension – may occur and if marked simulates intestinal obstruction.
(e)Boa’s sign – Area of hyperesthesia over right subscapular region.
WHAT TO EAT
For managing gallbladder stones, a diet that supports gallbladder health, reduces inflammation, and prevents further stone formation is important. Here’s a point-wise guide:
Low-Fat Diet: Avoid high-fat foods like fried items, fatty meats, and full-fat dairy. Opt for lean proteins like chicken, turkey, and fish.
High-Fiber Foods: Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes to support digestion and reduce cholesterol levels.
Healthy Fats: Include moderate amounts of healthy fats from sources like avocados, olive oil, and nuts, which can support gallbladder function.
Hydration: Drink plenty of water to maintain bile flow and prevent stone formation.
Avoid Refined Sugars: Limit sugary snacks and drinks, as they can contribute to the formation of gallstones.
Small, Frequent Meals: Eat smaller meals throughout the day to reduce gallbladder strain.
Consult a healthcare provider for a personalized treatment plan.
DIET AND REGIMEN
- Eat more foods that are high in fiber, such as. …
- Eat fewer refined carbohydrates and less sugar.
- Eat healthy fats, like fish oil and olive oil, to help your gallbladder contract and empty on a regular basis.
- Avoid unhealthy fats, like those often found in desserts and fried foods.
Why Choose Spiritual Homeopathy?
At Spiritual Homeopathy, we offer a unique approach to healing that integrates traditional homeopathic principles with a deep understanding of the spiritual aspects of health. Our team of experienced homeopathic practitioners combines expertise with empathy, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care tailored to your individual needs.
Our Approach to Treatment
We believe that true healing occurs when all aspects of a person—physical, emotional, and spiritual—are in balance. That’s why our treatment approach goes beyond simply addressing symptoms to identify and treat the underlying imbalances contributing to your health concerns. By addressing the root cause of illness and supporting your body’s innate healing ability, we empower you to achieve lasting health and vitality.
Services We Offer
Consultations: Our experienced best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad offer comprehensive consultations to assess your health concerns, medical history, and individual needs. we also take online consultation and We take the time to listen to your story, understand your unique health goals, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Remedies: At Spiritual Homeopathy, we provide a wide range of homeopathic remedies carefully selected to address a variety of health conditions. From acute ailments to chronic diseases, our remedies are safe, gentle, and effective, offering natural relief without the side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Follow-Up Care: We believe in the importance of ongoing support and monitoring throughout your healing journey. Our team is dedicated to providing regular follow-up care to track your progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that you are on the path to optimal health and well-being.
Our Commitment to You
At Spiritual Homeopathy, your health and wellness are our top priorities. We are committed to providing you with compassionate care, personalized treatment, and the support you need to achieve your health goals. Whether you are seeking relief from a specific health concern or simply looking to optimize your overall well-being, we are here to support you every step of the way
FAQ
What is Gallstones?
A small, hard crystalline mass formed abnormally in the gall bladder or bile ducts from bile pigments, cholesterol, and calcium salts. Gallstones can cause severe pain and blockage of the bile duct.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Gallstones?
- Kali mur
- Apis
- Sulphur
- Belladona
- Merc-sol
- Mag Phos
- Calcarea Phos
What causes Gallstones?
- Bile contains too much cholesterol
- Bile contains too much bilirubin
- Gallbladder doesn’t empty correctly
What are the symptoms of Gallstones?
Fever with often chills at Onset, and tachycardia.
- Tenderness and muscle guarding in right upper quadrant.
- Murphy’s sign
- Abdominal distension
- Boa’s sign
Give the types of Gallstones?
- Cholesterol gallstones
- Pigment gallstones
REFFERNCE
[1] Davidsons Principles and Practice of Medicine (PDFDrive.com)
[2] Medicine Golwala
[3]https://www.healthgrades.com/right-care/gallbladder-removal-surgery/cholelithiasis
[4]https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/gallstones/eating-diet-nutrition
[5]T.F.Allen