Homeopathic treatment for Obesity
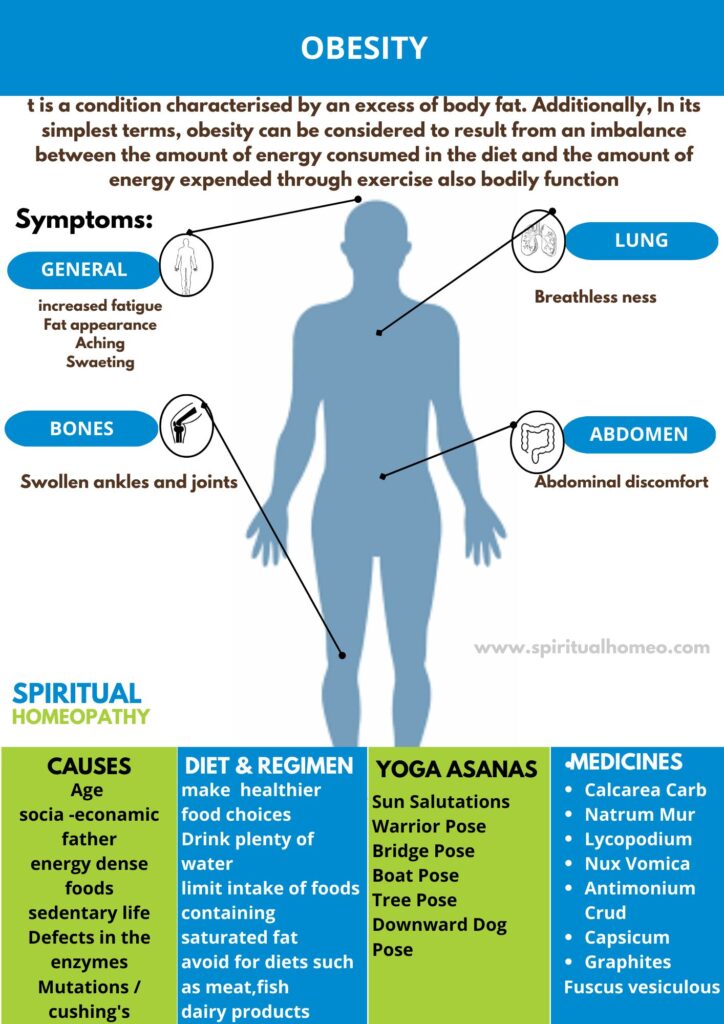
It is a condition characterized by an excess of body fat. Additionally, In its simplest terms, obesity can be considered to result from an imbalance between the amount of energy consumed in the diet and the amount of energy expended through exercise also bodily functions.
- Overview
- Causes
- Types
- Sign & Symptoms
- What to eat
- Diet and Regiment
- Homeopathic Treatment
- FAQ
- Reference
In brief,Obesity is widely regarded as a pandemic, with potentially disastrous consequences for human health.
Demography
In developing countries, average national rates of heavier person are low, but these figures may disguise high rates of heavier person in urban communities; for example, nearly one quarter of women in urban India are higher weight body. In detail, There is increasing public awareness of the health implications of obesity. Many patients will seek medical help for their obesity, on other hand others will present with one of the complications of obesity.
In countries like the USA also the UK, fat deposition is affecting almost the entire population. Additionally, The weight distribution of almost the whole population is shifting upwards – the slim are becoming less slim while the fat is getting fatter. Specifically, In the UK, this translates into a 1-kilogram increase in weight per adult per year (on average over the adult population).
A continuous small daily positive energy balance of only 0.2–0.8 MJ (50–200 kcal; < 10% of intake) would lead to weight gain of 2–20 kg over a period of 4–10 years.
Age i.e.:
Basically; heavier person usually become higher weight body adults. In detail, Weight tends to increase throughout adult life, as BMR and physical activity decrease.
Socio-economic Factor i.e.:
Generally, India it is estimated that 5% of the population receives 40% of the available food energy, leading to obesity in the urban population in parallel with persisting undernutrition in some rural communities
Energy dense foods i.e.:
For example; drinks with highly refined sugar content and salty snacks.
Sedentary life i.e.:
In brief, Decrease in physical activity levels in recent years correlated positively with the number of hours spent watching television. inversely with levels of physical activity (e.g. stair climbing).
Genetic role i.e.:
Twin also adoption studies confirm a genetic influence on obesity.
A few rare single gene disorders i.e.:
This disorders have been identified that lead to severe childhood obesity i.e. melanocortin4 receptor (in other words; MC4R)
Defects in the enzymes processing proopiomelanocortin (POMC, the precursor for adrenocorticotrophic hormone (in other words; ACTH)) in the hypothalamus.
mutations in the leptin gene.
Additional genetic conditions i.e.:
like Prader– Willi also Lawrence–Moon–Biedl syndromes.
underlying disorder i.e.:
such as hypothyroidism or Cushing’s syndrome
Obesity can be categorized in various ways depending on its cause, the area of the body where fat is stored, and the overall health implications it has. Below are several types or classifications of obesity:
1. Classifications Based on BMI (Body Mass Index):
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a commonly used measurement to classify obesity. It’s calculated using a person’s weight and height and gives an estimate of body fat. Here are the common BMI categories for obesity:
Overweight: BMI of 25 to 29.9.
Obesity (Class 1): BMI of 30 to 34.9.
Obesity (Class 2): BMI of 35 to 39.9.
Severe Obesity (Class 3): BMI of 40 or higher (often referred to as morbid obesity or extreme obesity).
2. Visceral vs. Subcutaneous Obesity:
Obesity can also be classified based on where fat is stored in the body.
Visceral Obesity:
This type of obesity occurs when excess fat is stored around the internal organs (like the liver, pancreas, and intestines). Visceral fat is considered more dangerous because it’s linked to various health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.Characteristics: Enlarged abdomen, “apple-shaped” body, high waist-to-hip ratio.
Risks: Increased risk for cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and liver disease.
Subcutaneous Obesity:
Subcutaneous fat is the fat stored just beneath the skin. This type is generally considered less harmful than visceral fat, though excessive amounts can still increase health risks.Characteristics: Fat accumulated in areas such as the thighs, hips, and buttocks, leading to a “pear-shaped” body.
Risks: While it is less harmful than visceral fat, it can still contribute to joint problems, difficulty with mobility, and higher cholesterol levels.
3. Android vs. Gynoid Obesity:
This classification is based on the shape of the body and the distribution of fat:
Android Obesity:
Often referred to as “apple-shaped” obesity, it is characterized by fat accumulation around the abdomen and upper body. This type of obesity is more common in men and tends to be linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, and type 2 diabetes.Characteristics: Fat around the waist and upper body.
Risks: Higher risk for cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic issues.
Gynoid Obesity:
This type is often called “pear-shaped” obesity and is more common in women. It involves fat accumulation in the lower body (hips, thighs, and buttocks). While it’s generally considered less risky than android obesity, it can still lead to issues such as joint problems or cellulite.Characteristics: Fat primarily in the lower body (hips and thighs).
Risks: Although it has fewer associated risks than android obesity, it can still lead to mobility issues, joint pain, and complications during pregnancy.
4. Monogenic Obesity:
Monogenic obesity is caused by a single genetic mutation. This rare form of obesity is often present from an early age and is associated with problems in regulating appetite or energy balance.
Characteristics: Obesity that begins in childhood, with a strong genetic predisposition.
Risks: It may require special medical management and can lead to severe obesity at an early age.
5. Endocrine (Hormonal) Obesity:
This type of obesity occurs due to hormonal imbalances or disorders that affect metabolism, appetite regulation, or fat storage. Conditions such as hypothyroidism, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and Cushing’s syndrome can lead to hormonal obesity.
Common Conditions:
Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid leads to slow metabolism and weight gain.
PCOS: Hormonal imbalances in women can lead to weight gain, especially in the abdominal area.
Cushing’s Syndrome: An overproduction of cortisol can lead to fat accumulation, particularly around the face and abdomen.
Characteristics: Slow metabolism, weight gain without clear cause, and other symptoms specific to the underlying condition.
Risks: Health complications are linked to the underlying hormonal disorder, including diabetes, high blood pressure, and infertility (in PCOS).
6. Emotional or Psychological Obesity:
Psychological factors, such as emotional stress, depression, anxiety, or trauma, can contribute to overeating, which can lead to obesity. People may use food as a coping mechanism for emotional distress (known as emotional eating).
Characteristics: Obesity associated with overeating in response to emotional triggers, such as stress, sadness, or boredom.
Risks: Increased risk of developing binge eating disorder, as well as other mental health conditions like depression and anxiety.
7. Lifestyle-Related Obesity:
Obesity caused by unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and sedentary behavior, is the most common form of obesity. It often results from an imbalance between calorie intake and calorie expenditure.
Characteristics: Overeating, frequent consumption of processed and high-calorie foods, lack of physical activity.
Risks: Greater risk of developing heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, and other chronic conditions.
8. Obesity due to Medications:
Certain medications can contribute to weight gain and obesity. These may alter the body’s metabolism, increase appetite, or make it easier to gain weight.
Common Medications:
Antidepressants (e.g., SSRIs, tricyclic antidepressants)
Antipsychotics (e.g., olanzapine, clozapine)
Corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone)
Insulin (for diabetes)
Characteristics: Gradual weight gain after starting certain medications.
Risks: Increased risk of obesity-related diseases, especially if the medication is taken long-term.
9. Pregnancy-Related Obesity:
Pregnancy can lead to weight gain due to changes in hormones, metabolism, and dietary habits. While weight gain is expected and necessary during pregnancy, excessive weight gain can increase the risk of obesity later in life, both for the mother and child.
Characteristics: Weight gain during pregnancy that exceeds recommended guidelines.
Risks: Postpartum weight retention, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic issues.
Fat appearance.
Weight of 20% or more than ideal for height and body frame. In detail; Some heavier person have no physical symptoms but may have associated emotional problems and poor exercise tolerance.
Others may possibly experience:
Abdominal discomfort
Aching
Swollen ankles and joints
Breathlessness
Sweating
Increased fatigue
When managing obesity, a balanced diet is essential to help achieve and maintain a healthy weight. The goal is to consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods while reducing calorie intake and improving overall health. Focusing on whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, can help support weight loss, improve metabolism, and provide the body with essential nutrients.
Here are some general guidelines for what to eat when trying to manage obesity:
1. Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are low in calories, high in fiber, and rich in vitamins and minerals. They can help fill you up without consuming too many calories. Aim for a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables to get a broad range of nutrients and antioxidants.
Examples: Leafy greens (spinach, kale), berries (strawberries, blueberries), apples, carrots, bell peppers, cucumbers, and broccoli.
2. Lean Proteins
Protein is important for building and repairing muscle and can help you feel fuller for longer, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Choose lean protein sources to keep your calorie intake in check.
Examples: Skinless poultry (chicken or turkey), fish (especially fatty fish like salmon, mackerel), eggs, tofu, tempeh, beans, and legumes (lentils, chickpeas).
3. Whole Grains
Whole grains are high in fiber and can help regulate blood sugar levels, keeping you satisfied and energized. They are better than refined grains, which can lead to blood sugar spikes and contribute to weight gain.
Examples: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, whole wheat, barley, and farro.
4. Healthy Fats
Incorporating healthy fats in moderation can help improve heart health and support brain function. Healthy fats also help you feel satiated, preventing overeating.
Examples: Avocados, nuts (almonds, walnuts), seeds (chia, flax), olive oil, and fatty fish (salmon, sardines).
5. Low-Fat Dairy or Dairy Alternatives
Dairy products are a good source of calcium and protein, but choosing low-fat or fat-free options can help you reduce overall calorie intake.
Examples: Skim or 1% milk, low-fat yogurt, cottage cheese, or dairy alternatives like almond milk, soy milk, or oat milk (unsweetened).
6. Legumes and Beans
Beans, lentils, and legumes are excellent sources of protein and fiber, which can help control hunger and aid in weight management. They also have a low glycemic index, which can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Examples: Black beans, kidney beans, chickpeas, lentils, and peas.
7. Water
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help you stay hydrated and control your appetite. Sometimes, thirst can be mistaken for hunger, so drinking water before meals can also help prevent overeating.
Tip: Aim for at least 8 cups (about 2 liters) of water per day.
Foods to Avoid or Limit for Obesity:
While focusing on nutrient-dense foods, it’s also important to limit or avoid foods that are high in empty calories and can contribute to weight gain.
Processed Foods and Junk Food: These foods tend to be high in refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and empty calories that provide little nutritional value.
Examples: Fast food, chips, sugary snacks, processed meats (hot dogs, sausages), and sugary baked goods (cookies, cakes, pastries).
Sugary Drinks: Beverages like sodas, sweetened teas, and energy drinks contain a lot of calories without offering any nutritional benefits.
Alternative: Choose water, herbal teas, or beverages without added sugars (e.g., sparkling water or unsweetened iced tea).
Refined Carbohydrates: Refined carbs like white bread, pasta, and white rice can cause blood sugar spikes, leading to increased hunger and overeating.
Alternative: Opt for whole grains like brown rice, whole wheat bread, quinoa, or sweet potatoes.
High-Calorie Alcohol: Alcoholic beverages, especially cocktails or sugary mixed drinks, can be high in empty calories and hinder weight loss progress.
Alternative: If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation and opt for lower-calorie options like wine or light beer.
Managing obesity effectively requires a combination of dietary changes, physical activity, and behavioral adjustments. A healthy diet and regular exercise can help reduce body weight, improve overall health, and prevent complications associated with obesity (such as diabetes, heart disease, and joint issues). Here’s a comprehensive diet and regimen for managing obesity.
Diet for Obesity:
When addressing obesity, the goal is to create a sustainable, healthy eating pattern that promotes weight loss and supports overall health. Focus on nutrient-dense foods that provide essential vitamins and minerals while being lower in calories.
Key Principles of an Obesity-Friendly Diet:
Calorie Control:
To lose weight, you need to create a calorie deficit, meaning you consume fewer calories than you burn. Aim for a gradual weight loss of 1–2 pounds per week, which is considered safe and sustainable.High in Fiber:
Foods rich in fiber help with satiety, so you feel full longer and are less likely to overeat. Fiber also aids in digestion and can help regulate blood sugar.Protein-Rich Foods:
Protein helps to build and repair muscles, and it can help reduce hunger. Include lean protein sources in your meals to support weight loss and maintain muscle mass.Healthy Fats:
Healthy fats, when eaten in moderation, can keep you satisfied, prevent cravings, and support heart health.
What to Eat:
Fruits and Vegetables
These are low in calories and rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Aim to fill half of your plate with vegetables and fruits. Choose a variety of colors for optimal nutrient intake.Examples: Leafy greens (spinach, kale), cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower), berries, apples, and carrots.
Whole Grains
Whole grains are high in fiber and help to regulate blood sugar levels, preventing overeating and hunger spikes.Examples: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley, and whole wheat bread or pasta.
Lean Proteins
Protein supports muscle mass and promotes feelings of fullness. Choose lean protein sources to avoid excess fat.Examples: Skinless poultry (chicken or turkey), fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna), eggs, tofu, tempeh, legumes (beans, lentils), and low-fat dairy.
Healthy Fats
Healthy fats help keep you satisfied and support overall health. Use these in moderation.Examples: Avocados, nuts (almonds, walnuts), seeds (chia, flax), olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon.
Low-Fat Dairy
Low-fat dairy provides calcium and protein without excess calories from fat.Examples: Low-fat yogurt, skim milk, and low-fat cheese.
Legumes and Beans
These are excellent sources of fiber and protein, making them ideal for a weight loss diet.Examples: Black beans, kidney beans, chickpeas, lentils, and peas.
Water
Drinking water throughout the day helps maintain hydration, reduces hunger, and supports metabolism. Aim to drink at least 8 cups (2 liters) of water per day.Tip: Drink a glass of water before meals to reduce appetite and prevent overeating.
Foods to Avoid or Limit:
Sugary Foods and Drinks
These foods are high in empty calories and can cause blood sugar spikes and crashes.Avoid: Sodas, sweetened beverages, candy, cakes, cookies, and sugary snacks.
Processed and Refined Foods
Foods that are processed or refined often contain high amounts of sugar, unhealthy fats, and preservatives.Avoid: Fast food, chips, white bread, pastries, and packaged snacks.
Alcohol
Alcohol is high in calories and can interfere with your metabolism and decision-making, often leading to overeating.Limit: Stick to low-calorie drinks (e.g., wine or light beer) and consume in moderation.
Trans Fats and Saturated Fats
Avoid foods that contain unhealthy fats, as they can increase the risk of heart disease and contribute to weight gain.Avoid: Fried foods, processed snacks, and fatty cuts of meat.
Regimen for Managing Obesity:
In addition to diet, adopting a regular exercise routine and healthy lifestyle habits is crucial to managing obesity. Here’s a recommended regimen:
1. Regular Physical Activity:
Exercise helps burn calories, improve metabolism, and maintain muscle mass while losing fat. A combination of aerobic exercise and strength training is most effective for weight loss and overall health.
Cardio (Aerobic Exercise): Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity (e.g., brisk walking, cycling, swimming) per week or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity (e.g., running, hiking, intense cycling).
Examples: Walking, jogging, swimming, cycling, dancing, or using cardio machines like the treadmill or elliptical.
Strength Training (Muscle Building): Aim to do strength training exercises at least 2 days a week. This helps build lean muscle mass, which in turn can increase metabolism.
Examples: Weight lifting, bodyweight exercises (squats, lunges, push-ups), resistance band exercises, and yoga.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises: Incorporating stretching or yoga can improve flexibility, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being.
Examples: Yoga, Pilates, or simple stretching routines.
2. Behavioral Changes and Mindful Eating:
Making behavioral changes is crucial for long-term weight management. Mindful eating and lifestyle adjustments can prevent overeating and support healthy habits.
Mindful Eating: Focus on eating slowly and paying attention to hunger and fullness cues. Avoid distractions like watching TV or using a phone while eating.
Portion Control: Use smaller plates, bowls, and utensils to help control portion sizes. Try to eat slowly and stop eating when you feel full.
Regular Meals and Snacks: Avoid skipping meals, as it can lead to overeating later. Opt for small, balanced meals throughout the day to keep hunger at bay.
3. Sleep Hygiene:
Getting enough sleep is essential for weight management. Poor sleep can interfere with hormones that regulate hunger and appetite, leading to weight gain.
Aim for 7–9 hours of sleep per night.
Establish a regular bedtime routine and avoid caffeine, alcohol, or large meals close to bedtime.
4. Stress Management:
Chronic stress can contribute to overeating and weight gain. Engage in stress-reducing activities to help manage your emotions and prevent emotional eating.
Examples: Meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, and spending time outdoors.
5. Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Sometimes thirst is mistaken for hunger, so staying hydrated can help prevent overeating.
Why Choose Homeopathy?
Homeopathy offers natural and holistic healing, treating the root cause of ailments without side effects. It strengthens the body’s defense system, is gentle for all ages, and personalized to each individual’s needs. Choose homeopathy for safe, effective, and long-lasting health solutions.
Spiritual Homeopathy: Your Path to Natural Healing
At Spiritual Homeopathy, where we believe in the power of holistic healing and personalized care. Our mission is to provide compassionate and effective homeopathic treatment to help you achieve optimal health and well-being. With a focus on addressing the root cause of illness and promoting harmony between mind, body, and spirit, we are dedicated to guiding you on your journey towards vibrant health and vitality.
Why Choose Spiritual Homeopathy?
At Spiritual Homeopathy, we offer a unique approach to healing that integrates traditional homeopathic principles with a deep understanding of the spiritual aspects of health. Our team of experienced homeopathic practitioners combines expertise with empathy, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care tailored to your individual needs.
Our Approach to Treatment
We believe that true healing occurs when all aspects of a person—physical, emotional, and spiritual—are in balance. That’s why our treatment approach goes beyond simply addressing symptoms to identify and treat the underlying imbalances contributing to your health concerns. By addressing the root cause of illness and supporting your body’s innate healing ability, we empower you to achieve lasting health and vitality.
Services We Offer
Consultations: Our experienced best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad offer comprehensive consultations to assess your health concerns, medical history, and individual needs. we also take online consultation and We take the time to listen to your story, understand your unique health goals, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Remedies: At Spiritual Homeopathy, we provide a wide range of homeopathic remedies carefully selected to address a variety of health conditions. From acute ailments to chronic diseases, our remedies are safe, gentle, and effective, offering natural relief without the side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Follow-Up Care: We believe in the importance of ongoing support and monitoring throughout your healing journey. Our team is dedicated to providing regular follow-up care to track your progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that you are on the path to optimal health and well-being.
Our Commitment to You
At Spiritual Homeopathy, your health and wellness are our top priorities. We are committed to providing you with compassionate care, personalized treatment, and the support you need to achieve your health goals. Whether you are seeking relief from a specific health concern or simply looking to optimize your overall well-being, we are here to support you every step of the way.
1 . Nux Vomica: This remedy is commonly used for acidity caused by overeating, spicy food, alcohol, and coffee. It may help with symptoms like heartburn, sour burping, nausea, and stomach pain. It is often recommended for individuals who are irritable and have a sedentary lifestyle.
2. Carbo Vegetabilis: This remedy is used for individuals who experience bloating, gas, and a feeling of fullness in the abdomen. It can be helpful for acidity accompanied by belching, flatulence, and a weak digestion.
3. Robinia: This remedy is often indicated for individuals who experience intense burning sensations in the stomach and esophagus. It may be helpful for acidity that worsens at night and is accompanied by regurgitation of sour or bitter fluid.
4.Arsenicum Album: This remedy may be beneficial for individuals with burning pains and a feeling of weakness or restlessness. It can be used for acidity associated with anxiety, fear, and a desire for small sips of water.
5.Pulsatilla: This remedy is often recommended for individuals who experience acidity after eating rich, fatty foods. They may have a coated tongue, no thirst, and a preference for cool open air.
It’s recommended to consult with a qualified homeopathic practitioner who can take your detailed case history, consider your individual symptoms, and provide appropriate guidance and treatment. They will be able to customize the treatment according to your unique needs.
Consult the Best Homeopathy Doctors in India at Spiritual Homeopathy Clinics, Hyderabad
We offer both in-clinic and online consultations, specializing in chronic ailments such as thyroid issues, diabetes, sexology problems, dermatology complaints, gastric issues, rheumatoid and osteoarthritis, respiratory complaints, migraines, and more. Our best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad provides personalized care and has treated patients from over 60 countries, including India, Nepal, Bhutan, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Canada, England, Holland, China, Sri Lanka, Germany, France, USA, UK, Australia, New Zealand, Russia, Afghanistan, Myanmar, and many other Asian and European countries. We also specialize in Homeopathy treatment for kids and children.
Book your video consultation or in-clinic appointment now and experience holistic healing with our experienced team.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Obesity
1. What is obesity?
Obesity is a condition where excess body fat has accumulated to the point that it may have a negative effect on health. It’s typically diagnosed when a person has a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 30 or higher.
2. What causes obesity?
Obesity is usually caused by a combination of:
Consuming more calories than the body uses (poor diet)
Physical inactivity
Genetics
Hormonal imbalances
Certain medications or medical conditions
3. What are the health risks of obesity?
Obesity increases the risk of:
Type 2 diabetes
Heart disease and stroke
High blood pressure
Certain cancers (e.g., breast, colon)
Sleep apnea
Osteoarthritis
Mental health issues like depression
4. How is obesity diagnosed?
The most common method is calculating Body Mass Index (BMI):
25–29.9 = Overweight
30 or more = Obese
Other measures include waist circumference and body fat percentage.
5. Can obesity be caused by genetics?
Yes, genetics can influence body weight, metabolism, and appetite, but lifestyle factors like diet and activity level still play a major role.
6. Is obesity preventable?
In many cases, yes. Preventing obesity involves:
Eating a balanced, healthy diet
Staying physically active
Managing stress and sleep
Avoiding high-calorie, processed foods
7. What are some effective treatments for obesity?
Lifestyle changes (diet and exercise)
Behavioral therapy
Medications (e.g., orlistat, semaglutide)
Bariatric surgery (for severe cases)
8. How much weight loss is needed to improve health?
Even a modest weight loss of 5–10% of your body weight can lead to significant health improvements like lower blood pressure, better blood sugar control, and reduced cholesterol levels.
9. Is obesity the same as being overweight?
Not exactly. Overweight means having more body weight than is considered healthy for a given height, while obesity specifically refers to having an excessive amount of body fat.
10. Can children and teens be obese?
Yes. Childhood obesity is a serious concern and can lead to long-term health problems. Early intervention with healthy eating and physical activity is key.
Reference for Obesity
World Health Organization (WHO).
Obesity and overweight.
Updated 9 June 2021.
Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
Summary of key points from WHO:
Obesity is defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a health risk.
Body Mass Index (BMI) ≥ 30 is considered obese.
It increases the risk of heart disease, diabetes, musculoskeletal disorders (like osteoarthritis), and certain cancers.
It’s largely preventable through a healthy diet and physical activity.
If you’re looking for more academic or clinical sources, here are two widely used references:
1. CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
Adult Obesity Facts
https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html
2. Bray GA, Kim KK, Wilding JPH.
Obesity: a chronic relapsing progressive disease process.
Obes Rev. 2017 Jul;18(7):715-723.
doi: 10.1111/obr.12551