Homeopathy treatment for Shoulder pain
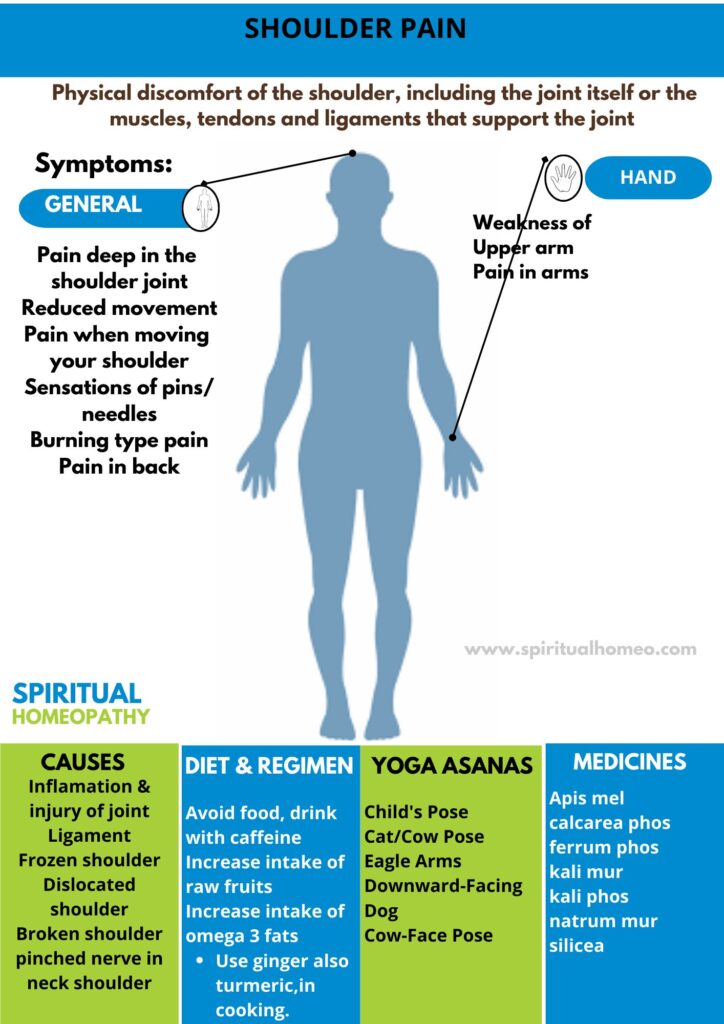
Shoulder pain is defined as Physical discomfort of the shoulder, including the joint itself or the muscles, tendons and ligaments that support the joint.
- Overview
- Causes
- Types
- Sign & Symptoms
- What to eat
- Diet and Regiment
- Homeopathic Treatment
- FAQ
- Reference
During the evaluation of shoulder disorders, the examiner should carefully note any history of trauma, fibromyalgia, infection, inflammatory disease, occupational hazards, or previous cervical disease.
Shoulder pain may originate in the Glenohumeral or acromioclavicular joints, sub acromial (subdeltoid) bursa, periarticular soft tissues (e.g., fibromyalgia, rotator cuff tear/tendinitis), or cervical spine.
Cuases
-
Shoulder pain is referred frequently from the cervical spine but may also be referred from intrathoracic lesions (e.g., a Pancoast tumor) or from gallbladder, hepatic, or diaphragmatic disease.
- Sub acromial bursitis is a frequent cause of shoulder pain. Whereas OA and RA commonly affect the acromioclavicular joint, OA seldom involves the Glenohumeral joint, unless there is a traumatic or occupational cause.
- Rotator cuff tendinitis or tear is a very common cause of shoulder pain. Nearly 30 percent of the older people will have shoulder pain, with rotator cuff tendinitis or tear as the primary cause.
- Another common cause of shoulder pain is impingement syndrome where the rotator cuff gets caught between the acromion and humeral head .
- Sometimes shoulder pain is the result of injury to another location in your body, usually the neck or biceps. This is known as referred pain. Referred pain generally doesn’t get worse when you move your shoulder.
Other causes of shoulder pain include:
- Arthritis
- Torn cartilage
- Torn rotator cuff
- Swollen bursa sacs or tendons
- Bone spurs (bony projections that develop along the edges of bones)
- Pinched nerve in the neck or shoulder
- Broken shoulder or arm bone
- Dislocated shoulder
- Injury due to overuse or repetitive use
- Spinal cord injury
- Heart attack
Types
1. Rotator Cuff Injuries
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder. Injuries to the rotator cuff are a frequent cause of shoulder pain.
-
Rotator Cuff Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons in the rotator cuff, often caused by repetitive overhead motions.
-
Rotator Cuff Tear: A tear in one or more of the rotator cuff muscles or tendons, often due to injury or degeneration over time.
2. Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
Frozen shoulder is a condition characterized by stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint. The capsule of the shoulder becomes thickened and tight, limiting movement.
-
Primary Frozen Shoulder: Occurs without any apparent cause.
-
Secondary Frozen Shoulder: Develops as a result of another condition, such as shoulder injury, surgery, or diabetes.
3. Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
Shoulder impingement occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff become irritated or inflamed as they pass through the shoulder joint. This can lead to pain, especially when lifting the arm.
4. Bursitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that helps reduce friction and cushion the muscles and tendons. Inflammation of the subacromial bursa in the shoulder can cause pain and limited mobility.
-
Subacromial Bursitis: A common form of shoulder bursitis that causes pain at the top and outer part of the shoulder.
5. Shoulder Arthritis
Arthritis in the shoulder joint can cause pain, stiffness, and decreased range of motion. Two main types are:
-
Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of the cartilage in the shoulder joint due to wear and tear.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and damage to the shoulder joint.
6. Shoulder Dislocation or Instability
Shoulder dislocation occurs when the ball of the humerus (upper arm bone) is forced out of the socket. Instability occurs when the shoulder repeatedly slips out of place, often due to previous dislocations or ligament damage.
-
Anterior Dislocation: The most common form, where the head of the humerus is displaced forward.
-
Posterior Dislocation: Less common, where the humeral head is displaced backward.
7. Tendonitis
Tendonitis is the inflammation of the tendons in the shoulder, often due to overuse or injury.
-
Supraspinatus Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle, a part of the rotator cuff.
-
Biceps Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendon that connects the biceps muscle to the shoulder.
8. Labral Tear
The labrum is cartilage that forms a cup to hold the ball of the shoulder joint. A tear in the labrum can cause pain, instability, and weakness.
-
SLAP Tear: A tear in the superior labrum from anterior to posterior, often caused by overhead motions.
-
Bankart Tear: A tear in the labrum, often caused by shoulder dislocations.
9. Calcific Tendonitis
Calcific tendonitis occurs when calcium deposits build up in the tendons of the rotator cuff. This can cause significant pain, particularly when lifting or moving the arm.
10. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
This condition occurs when the blood vessels or nerves between the collarbone and the first rib become compressed. It can lead to shoulder pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the arm and hand.
11. Referred Pain
Shoulder pain can sometimes be referred from other parts of the body. For example:
-
Heart-related Pain: Pain from a heart attack can sometimes radiate to the shoulder, especially the left shoulder.
-
Gallbladder Issues: Gallbladder problems or gallstones can cause pain that radiates to the right shoulder.
12. Fractures
Fractures or breaks in the bones of the shoulder, such as the clavicle (collarbone) or humerus (upper arm bone), can result in sharp, acute pain and limited mobility.
-
Clavicle Fracture: A break in the collarbone, often due to trauma or falls.
-
Proximal Humerus Fracture: A break in the upper part of the arm bone, often caused by falls or accidents.
13. Myofascial Pain Syndrome
This type of shoulder pain is caused by trigger points or muscle knots in the muscles around the shoulder. It can lead to chronic, aching pain that may worsen with certain movements.
Sign and Symptoms
Shoulder pain can manifest in various ways depending on the underlying cause. The signs and symptoms of shoulder pain can vary in intensity, duration, and type, but they generally involve discomfort, weakness, and limitations in movement. Below are some common signs and symptoms associated with different causes of shoulder pain:
1. General Shoulder Pain
-
Ache or tenderness: A dull or throbbing pain in the shoulder area, which may be constant or intermittent.
-
Sharp or shooting pain: This may occur with specific movements, such as lifting the arm or reaching overhead.
-
Pain radiating down the arm: The pain might travel down the upper arm or toward the elbow in certain conditions, like nerve irritation or rotator cuff injuries.
2. Rotator Cuff Injuries (Tendonitis, Tear)
-
Pain when lifting the arm: Lifting your arm overhead or behind your back may worsen the pain.
-
Weakness in the shoulder: Difficulty performing activities that involve raising the arm, such as reaching, combing hair, or lifting objects.
-
Limited range of motion: Inability to move the shoulder fully in all directions due to pain or stiffness.
-
Night pain: Pain that worsens at night, often disturbing sleep, particularly when lying on the affected side.
3. Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
-
Pain and stiffness: Initially, there is pain followed by a significant reduction in the range of motion.
-
Difficulty moving the shoulder: Especially with raising the arm or rotating it.
-
Gradual onset: The pain and stiffness usually develop over time and may take months to resolve.
-
Progressive limitation: Over time, there’s an increasing inability to perform everyday tasks like reaching for objects or dressing.
4. Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
-
Pain when lifting the arm: Pain may occur when the arm is lifted overhead, or when trying to reach behind your back.
-
Pain on the outside of the shoulder: The pain is usually located on the outer or upper part of the shoulder.
-
Weakness: Difficulty lifting or reaching objects due to muscle weakness.
-
Tenderness: Tenderness to the touch on the top or front of the shoulder.
5. Bursitis (Inflammation of the Bursa)
-
Swelling: The affected shoulder may appear swollen or feel puffy.
-
Pain when moving: Pain may be felt during specific movements, especially overhead activities.
-
Tenderness: Tenderness at the front or outer side of the shoulder when pressing on the bursa.
-
Stiffness: Limited shoulder motion, often with pain when reaching or lifting.
6. Arthritis (Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis)
-
Pain with movement: Pain that worsens with activity or movement, especially in the morning or after rest.
-
Stiffness: Difficulty moving the shoulder, particularly after periods of rest (morning stiffness).
-
Grating sensation: A feeling of grinding or creaking within the joint as it moves (crepitus).
-
Swelling: Swelling or warmth around the shoulder joint, especially in rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Chronic pain: Ongoing pain that can be both mild and severe, depending on the progression of arthritis.
7. Shoulder Dislocation or Instability
-
Sudden, intense pain: If a dislocation occurs, there will typically be immediate and severe pain.
-
Deformity: The shoulder may look out of place or deformed (the humeral head may be displaced).
-
Inability to move the shoulder: The affected shoulder may feel locked or unable to move.
-
Recurrent dislocations: People with chronic shoulder instability may feel the shoulder “pop out” during certain movements.
8. Tendonitis (Biceps Tendonitis)
-
Pain in the front of the shoulder: Tenderness and pain in the front of the shoulder or upper arm, especially with overhead activities.
-
Weakness: Difficulty lifting or reaching with the affected arm.
-
Pain with resistance: Pain may worsen when the arm is pushed or pulled against resistance, such as lifting a weight or pushing.
9. Labral Tear (SLAP or Bankart Tear)
-
Deep shoulder pain: Pain deep within the shoulder joint, sometimes worsening with overhead motions.
-
Shoulder instability: A feeling that the shoulder might “pop out” of the joint or feels loose.
-
Weakness: Difficulty performing overhead motions or lifting objects.
-
Clicking or popping sensation: A clicking, popping, or grinding sensation when moving the shoulder.
10. Fractures (Clavicle or Humerus)
-
Sudden, severe pain: This often follows trauma or injury, such as a fall.
-
Deformity: A visible deformity, especially in the clavicle (collarbone) or upper arm.
-
Swelling and bruising: Swelling and bruising around the affected area.
-
Limited movement: Inability to move the shoulder due to pain, especially when lifting the arm.
11. Myofascial Pain Syndrome (Muscle Pain and Trigger Points)
-
Muscle soreness: A dull ache or pain in the shoulder muscles, especially after overuse or tension.
-
Trigger points: Specific spots on the shoulder muscles that are tender to touch or can refer pain to other areas of the body.
-
Pain with movement: Certain shoulder movements can trigger sharp or aching pain in the muscles.
-
Limited range of motion: Painful muscle contractions may restrict shoulder movement.
12. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (Compression of Nerves or Blood Vessels)
-
Pain or numbness: Pain, tingling, or numbness in the shoulder, arm, or hand.
-
Weakness: Weakness in the arm or hand due to nerve compression.
-
Coldness: A sensation of coldness or discoloration in the hand or fingers.
-
Pain with certain arm movements: Pain may be exacerbated by lifting or moving the arm in certain ways.
When dealing with shoulder pain, particularly if it’s related to inflammation, injury, or musculoskeletal issues, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods and nutrients that support joint health can be beneficial. Here’s a guide to what you should consider eating for shoulder pain relief:
1. Anti-Inflammatory Foods
These foods help reduce inflammation, which is often a major contributor to shoulder pain, especially in conditions like arthritis, tendonitis, or bursitis.
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3s have strong anti-inflammatory properties.
-
Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout.
-
Chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts: Plant-based sources of omega-3s.
-
Fish oil supplements: If you don’t eat fish regularly, omega-3 supplements can also help.
-
-
Ginger: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, ginger can help reduce swelling and discomfort.
-
Ginger tea or adding fresh ginger to smoothies or soups.
-
-
Turmeric: Contains curcumin, a compound with powerful anti-inflammatory effects.
-
Add turmeric to dishes like curries, soups, or smoothies.
-
Pair with black pepper to increase absorption.
-
2. Foods Rich in Antioxidants
Antioxidants help protect your cells from damage, especially in cases of chronic pain or inflammation.
-
Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries are rich in antioxidants, which can reduce inflammation and support healing.
-
Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are loaded with antioxidants like vitamin C and beta-carotene.
-
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, and pumpkin seeds offer antioxidants and healthy fats.
3. Foods Rich in Collagen and Gelatin
Collagen is essential for joint health and can help in the healing of tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. Foods that help promote collagen production may reduce shoulder pain associated with injuries.
-
Bone broth: Rich in collagen and amino acids that support joint health.
-
Gelatin: Found in dishes like jellies or in supplements, gelatin is beneficial for collagen formation.
-
Chicken and turkey: They contain amino acids like proline and glycine, which are important for collagen production.
4. Vitamin D and Calcium
Both of these nutrients are important for bone health and can reduce the risk of bone-related pain or fractures, particularly in conditions like arthritis.
-
Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of both vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids.
-
Eggs: Contain vitamin D, especially when from free-range or pasture-raised chickens.
-
Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese are rich in calcium, which is vital for bone health.
-
Leafy greens: Kale and bok choy are good non-dairy sources of calcium.
-
Fortified foods: Some plant-based milk (such as almond, soy, or oat milk) is fortified with both calcium and vitamin D.
5. Foods Rich in Vitamin C
Vitamin C is vital for tissue repair and can support the healing of injured muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
-
Citrus fruits: Oranges, lemons, grapefruits, and limes are excellent sources of vitamin C.
-
Bell peppers: One of the best vegetable sources of vitamin C.
-
Kiwi, strawberries, and pineapple: Other great sources of vitamin C.
6. Magnesium-Rich Foods
Magnesium helps relax muscles and can prevent muscle spasms and cramping, which may contribute to shoulder discomfort.
-
Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are high in magnesium.
-
Nuts and seeds: Almonds, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds.
-
Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas.
-
Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and oats.
7. Foods That Promote Healthy Circulation
Good circulation is essential for healing and reducing pain. Foods that help improve blood flow can contribute to faster healing of injured shoulder tissues.
-
Beets: Beets can help increase blood flow due to their nitrate content.
-
Citrus fruits and pomegranates: Help with circulation and overall vascular health.
-
Garlic: Known for its ability to improve blood flow and reduce inflammation.
8. Hydration
Staying well-hydrated helps with overall tissue health, reduces inflammation, and aids in the healing process.
-
Water: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your joints lubricated.
-
Herbal teas: Ginger, turmeric, or chamomile teas can be soothing and anti-inflammatory.
-
Coconut water: A natural source of electrolytes that supports hydration.
Diet for Shoulder Pain
A well-balanced diet focused on anti-inflammatory foods can help alleviate shoulder pain and improve joint health. The key is to incorporate nutrients that promote healing, reduce inflammation, and support muscle, tendon, and bone health.
1. Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Since inflammation is often a primary factor in shoulder pain, foods that reduce inflammation can be helpful:
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
-
Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines, trout) are rich in omega-3s, which help reduce inflammation.
-
Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are plant-based sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
-
Fish oil supplements can also be considered if you don’t consume enough fatty fish.
-
-
Turmeric and Ginger:
-
Turmeric contains curcumin, which is a powerful anti-inflammatory compound. Add turmeric to dishes like soups, curries, or smoothies.
-
Ginger has natural anti-inflammatory effects. You can add fresh ginger to smoothies, teas, or meals.
-
-
Berries and Other Antioxidants:
-
Blueberries, strawberries, blackberries, and raspberries are rich in antioxidants that fight inflammation.
-
Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are also high in antioxidants.
-
Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits) and bell peppers (rich in vitamin C) help in tissue repair and immune support.
-
2. Nutrients for Joint and Bone Health
Strong bones and joints are essential for overall shoulder health:
-
Vitamin D and Calcium:
-
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in vitamin D, which helps calcium absorption and bone health.
-
Eggs, particularly the yolk, contain vitamin D.
-
Leafy greens (like kale and bok choy) and dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt) are excellent sources of calcium.
-
Fortified plant-based milks (almond, soy, oat) often contain added vitamin D and calcium.
-
-
Magnesium:
-
Magnesium is important for muscle relaxation and reducing cramps and spasms. Foods rich in magnesium include leafy greens (spinach), pumpkin seeds, almonds, and whole grains (brown rice, quinoa).
-
-
Collagen and Gelatin:
-
Collagen supports tendon, ligament, and cartilage health. Bone broth is an excellent source of collagen and other healing nutrients.
-
Gelatin (found in homemade soups, stocks, or supplements) helps in tissue repair and supports joint health.
-
3. Hydration
Proper hydration is essential for joint lubrication and to keep tissues healthy:
-
Water: Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day. Dehydration can make muscles and tendons stiffer, potentially worsening shoulder pain.
-
Herbal Teas: Herbal teas like ginger tea, chamomile, or turmeric tea have anti-inflammatory benefits and promote relaxation.
4. Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can exacerbate inflammation and worsen shoulder pain:
-
Refined sugars: Avoid sugary snacks, soft drinks, and pastries.
-
Processed foods: These often contain trans fats, additives, and preservatives that can increase inflammation.
-
Excessive alcohol: Alcohol can promote inflammation and interfere with the body’s healing process.
-
Red meat: Consuming too much red meat, particularly fatty cuts, can promote inflammation.
Regimen for Shoulder Pain
In addition to diet, maintaining a proper daily regimen with physical activity and self-care strategies is essential for managing shoulder pain.
1. Rest and Avoid Overuse
-
Rest the shoulder: Avoid activities that strain the shoulder, especially overhead movements or lifting heavy weights. Give your shoulder time to heal if it’s injured.
-
Modify activities: If certain movements trigger pain, modify how you do them (e.g., use ergonomic tools or avoid excessive lifting).
2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Engaging in gentle stretching and strengthening exercises is key to relieving pain and improving mobility.
-
Range-of-motion exercises: Start with exercises that gently increase the range of motion of the shoulder without straining it. Examples include shoulder circles, wall slides, and pendulum swings.
-
Rotator cuff exercises: Strengthening the muscles around the shoulder can prevent injuries and support healing. Exercises like external rotations, scapular squeezes, and shoulder abductions can be beneficial.
-
Stretching: Stretching the chest and upper back can help reduce shoulder tension and improve flexibility. Perform gentle stretches, such as chest openers and upper back stretches.
-
Posture exercises: Poor posture can contribute to shoulder pain. Focus on exercises that strengthen the back and core, such as rows, reverse flys, and posture-correcting movements.
3. Cold and Heat Therapy
-
Cold therapy (ice packs): Apply ice for 15-20 minutes a few times a day, especially after activity or when the pain is acute. This helps reduce swelling and inflammation.
-
Heat therapy (heating pads): Use heat after the initial inflammation has decreased to relax muscles and increase blood flow to the area. This can be particularly helpful for chronic pain.
4. Physical Therapy
-
Consult a physical therapist: A physical therapist can create a personalized program of exercises to help strengthen your shoulder and improve mobility. They can also help with techniques for posture correction, ergonomic support, and injury prevention.
5. Pain Management
-
Over-the-counter medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. Always consult a healthcare provider before using them regularly.
-
Topical treatments: Pain relief creams or gels containing menthol or capsaicin can provide temporary relief.
6. Ergonomics and Posture
-
Adjust workstation ergonomics: Ensure that your desk, computer, and chair setup promote good posture. Adjust the height of your chair and monitor so you don’t have to strain your shoulders.
-
Posture correction: Maintain a neutral spine and avoid slouching to prevent shoulder tension. Practice mindful posture throughout the day, especially when sitting for long periods.
7. Sleep Position
-
Sleep posture: Sleeping in a position that supports your shoulder is important. Avoid sleeping on the injured shoulder, and try to sleep on your back or the opposite side with a pillow supporting your arm.
-
Pillow support: Use pillows to prop up your arm and reduce strain on the shoulder while sleeping.
Why Choose Homeopathy?
Homeopathy offers natural and holistic healing, treating the root cause of ailments without side effects. It strengthens the body’s defense system, is gentle for all ages, and personalized to each individual’s needs. Choose homeopathy for safe, effective, and long-lasting health solutions.
Spiritual Homeopathy: Your Path to Natural Healing
At Spiritual Homeopathy, where we believe in the power of holistic healing and personalized care. Our mission is to provide compassionate and effective homeopathic treatment to help you achieve optimal health and well-being. With a focus on addressing the root cause of illness and promoting harmony between mind, body, and spirit, we are dedicated to guiding you on your journey towards vibrant health and vitality.
Why Choose Spiritual Homeopathy?
At Spiritual Homeopathy, we offer a unique approach to healing that integrates traditional homeopathic principles with a deep understanding of the spiritual aspects of health. Our team of experienced homeopathic practitioners combines expertise with empathy, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care tailored to your individual needs.
Our Approach to Treatment
We believe that true healing occurs when all aspects of a person—physical, emotional, and spiritual—are in balance. That’s why our treatment approach goes beyond simply addressing symptoms to identify and treat the underlying imbalances contributing to your health concerns. By addressing the root cause of illness and supporting your body’s innate healing ability, we empower you to achieve lasting health and vitality.
Services We Offer
Consultations: Our experienced best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad offer comprehensive consultations to assess your health concerns, medical history, and individual needs.we also take online consultation and We take the time to listen to your story, understand your unique health goals, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Remedies: At Spiritual Homeopathy, we provide a wide range of homeopathic remedies carefully selected to address a variety of health conditions. From acute ailments to chronic diseases, our remedies are safe, gentle, and effective, offering natural relief without the side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Follow-Up Care: We believe in the importance of ongoing support and monitoring throughout your healing journey. Our team is dedicated to providing regular follow-up care to track your progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that you are on the path to optimal health and well-being.
Our Commitment to You
At Spiritual Homeopathy, your health and wellness are our top priorities. We are committed to providing you with compassionate care, personalized treatment, and the support you need to achieve your health goals. Whether you are seeking relief from a specific health concern or simply looking to optimize your overall well-being, we are here to support you every step of the way.
Homeopathic Medicines for Shoulder pain :
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy.
Medicines:
Belladonna–
- If you have Bursitis with a feeling of warmth and trembling, along with severe pain, you can take Belladonna.
- Sometimes the area becomes red and with swelling.
Arnica Montana–
- This treatment is beneficial when Bursitis is linked to severe trauma or discomfort.
- The affected region appears to be red and painful.
- If you have these symptoms, you may try to avoid any touch on the painful area.
Kalmia latifolia–
- If you have pain that begins in the upper joint (particularly the hip or shoulder) and moves down indicates that you need this remedy.
- Right shoulder bursitis is widespread and spreads to the elbow, wrist, or side.
- Pain and inflammation can come on all of a sudden, sometimes shifting.
- Discomfort is worse from motion, worse at night, and of a neuralgic kind.
Bryonia-
- When the pain generated by Bursitis or stiff tissue has a stitching or tear-like feel, this medication is a decent choice.
- You may feel that the area is inflamed.
Ferrum phosphoricum-
- This remedy can help relieve swelling, specifically in the right shoulder, which can cause pain that progresses to your wrist or even your neck.
- Here you may feel relief with gentle movement and cold massage.
Rhus tox-
- This homoeopathic medication works wonders in the treatment of joint pain.
- This medication eases both acute and chronic muscle pain.
- We use this remedy if there is any stiffness in your joints and a lot of discomforts.
- This homoeopathic remedy addresses a wide range of joint pains, from rheumatoid arthritis to overuse injuries damages.
Calcarea Phos
- Shoulder-joint–Rheumatic pain in the arm near the shoulder-joint cannot lift the arm.
- Shooting and tearing from the shoulder-joint along the whole arm.
- consult best homeopathy doctors for best homeopathy treatment for Shoulder Pain at spiritual homeopathy Hyderabad
we also provide video consultation online. -
Consult the Best Homeopathy Doctors in India at Spiritual Homeopathy Clinics, Hyderabad
We offer both in-clinic and online consultations, specializing in chronic ailments such as thyroid issues, diabetes, sexology problems, dermatology complaints, gastric issues, rheumatoid and osteoarthritis, respiratory complaints, migraines, and more. Our best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad provides personalized care and has treated patients from over 60 countries, including India, Nepal, Bhutan, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Canada, England, Holland, China, Sri Lanka, Germany, France, USA, UK, Australia, New Zealand, Russia, Afghanistan, Myanmar, and many other Asian and European countries. We also specialize in Homeopathy treatment for kids and children.
Book your video consultation or in-clinic appointment now and experience holistic healing with our experienced team.
- Avoid food, drink with caffeine, meat, butter, cheese also milk as that will increase inflammation.
- Increase intake of raw fruits like cherries, papaya, pineapple. Additionally, They contain proteolytic enzymes which in turn help to reduce inflammation.
- Increase intake of omega 3 fats in supplemental form also from fish and walnuts.
- Take 2 tbsp of flax seed powder daily.
- Use ginger also turmeric, liberally in cooking.
- Take magnesium supplements to relax muscles. In detail, Avoid if you have kidney problems.
- Besides this, Try a spoonful of sesame seeds soaked overnight.
- Bromelain is an enzyme found in pineapple, It is a anti-inflammatory also alleviates pain and stiffness.
What is Shoulder pain ?
It is defined as Physical discomfort of the shoulder, including the joint itself or the muscles, tendons and ligaments that support the joint.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Shoulder pain ?
- Belladonna
- Arnica Montana
- Kalmia latifolia
- Bryonia
- Ferrum phosphoricum
- Rhus tox
What causes Shoulder pain ?
- Intrathoracic lesions
- Sub acromial bursitis
- Rotator cuff either tendinitis or tear
- Impingement syndrome
- Arthritis
- Swollen either bursa sacs or tendons
- Bone spurs
- Pinched nerve in the neck or shoulder
- Broken shoulder or arm bone
What are the symptoms of Shoulder pain ?
- Pain and tenderness of the lower neck and suprascapular area, referred to the shoulder also upper limb area
- Shoulder movement may be restricted
- Movement of the cervical spine and shoulder may reproduce more generalized upper back, neck, also shoulder pain.
- Upper limb paranesthesia
Reference
[1]https://www.healthline.com/health/chronic-pain/shoulder-pain
[2]Harrison-s_Principles_of_Internal_Medicine-_19th_Edition-_2_Volume_Sets
[3] A Complete Repertory of the Tissue Remedies of Schussler by S. F. Shannon
[4] https://aisclinic.in/homeopathy-treatment-and-medicine-for-shoulder-muscle-pain/