Neoplasm of Esophagus
A neoplasm is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor.
- Overview
- Causes
- Types
- Sign & Symptoms
- What to eat
- Diet and Regiment
- Homeopathic Treatment
- FAQ
- Reference
Esophageal cancer occurs when cells in the esophagus develop changes (mutations) in their DNA.
The changes make cells grow and divide out of control.
The accumulating abnormal cells form a tumor in the esophagus that can grow to invade nearby structures and spread to other parts of the body.
Spread of carcinoma
- Direct-
- The lesion may fill the lumen and infiltrate the wall of esophagus. It may also spread to the adjoining structures such as the trachea, left bronchus, aorta or pericardium.
- Involvement of the recurrent laryngeal nerves causes aspiration problems.
Lymphatic–
- Depending on the site involved, cervical, mediastinal or coeliac nodes may be involved.
- Cervical and thoracic lesions also spread to supraclavicular nodes.
- “Skip lesions” may also occur due to spread through the submucosal lymphatics.
- Blood borne-
- Metastases may develop in the liver, lungs, bone and brain.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption are high-risk factors and so are some particular dietary habits.
- High incidence is associated with tobacco chewing and smoking.
- About 5% of esophageal cancers arise in the pre-existing pathological lesions, such as benign strictures, hiatus hernia, cardiac achalasia and diverticula.
- Plummer–Vinson syndrome is another predisposing factor.
Neoplasms of the esophagus refer to abnormal growths or tumors in the esophagus, which can be benign or malignant. Esophageal neoplasms are typically classified based on the type of cells involved and whether the tumor is cancerous (malignant) or non-cancerous (benign).
Here are the main types of esophageal neoplasms:
1. Malignant (Cancerous) Neoplasms of the Esophagus:
These are the most common and dangerous types of esophageal tumors, as they are cancerous and can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body.
a. Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC)
Definition: This is the most common type of esophageal cancer worldwide, particularly in regions like Asia and parts of Africa.
Origin: It originates from the squamous cells that line the esophagus, which are thin, flat cells that are present in the upper and middle parts of the esophagus.
Risk Factors: Smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, poor diet (low in fruits and vegetables), and esophageal conditions like achalasia (a motility disorder) are major risk factors.
Symptoms: Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), weight loss, chest pain, hoarseness, and sometimes coughing up blood.
b. Esophageal Adenocarcinoma (EAC)
Definition: This type is more common in Western countries, particularly in the United States and Europe.
Origin: It arises from glandular cells in the lower part of the esophagus, typically near the junction with the stomach. It often develops from a condition called Barrett’s esophagus, in which the normal squamous cells of the esophagus are replaced by columnar cells due to chronic acid reflux (GERD).
Risk Factors: Chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Barrett’s esophagus, obesity, smoking, and age (more common in men and older individuals).
Symptoms: Similar to those of squamous cell carcinoma, such as dysphagia, weight loss, acid reflux, and chest pain.
c. Small Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus
Definition: This is a rare, but highly aggressive form of esophageal cancer that arises from neuroendocrine cells in the esophagus.
Characteristics: It is known for rapid growth and early metastasis to other organs.
Symptoms: Difficulty swallowing, weight loss, fatigue, chest pain, and possibly cough or hoarseness.
d. Other Rare Malignant Tumors
Sarcomas: Rare cancers that develop in the connective tissues of the esophagus (e.g., leiomyosarcoma, which arises from smooth muscle tissue).
Lymphoma: Esophageal lymphoma is rare and typically originates in the lymphoid tissue of the esophagus, though it can be secondary to other lymphomas.
Melanoma: A rare type of cancer that originates in melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) in the esophagus.
2. Benign (Non-Cancerous) Neoplasms of the Esophagus:
These tumors are not cancerous and generally do not spread to other parts of the body, though they can cause symptoms due to their size or location.
a. Esophageal Leiomyoma
Definition: The most common benign tumor of the esophagus, originating from smooth muscle cells.
Characteristics: Leiomyomas are usually small, and many people with these tumors do not experience any symptoms. When symptoms occur, they may include difficulty swallowing or chest pain.
Treatment: In many cases, leiomyomas do not require treatment unless they cause significant symptoms. Surgical removal may be necessary if the tumor is large.
b. Esophageal Papilloma
Definition: A benign tumor made up of papillary growths (finger-like projections of tissue).
Risk Factors: Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is sometimes associated with the development of esophageal papillomas.
Symptoms: Usually asymptomatic, but in some cases, it may cause difficulty swallowing or a feeling of obstruction.
Treatment: Removal may be necessary if the papilloma causes symptoms or is at risk of becoming malignant.
c. Esophageal Hemangioma
Definition: A benign tumor composed of blood vessels, which is very rare in the esophagus.
Symptoms: Most hemangiomas do not cause symptoms. If they are large, they may cause bleeding or difficulty swallowing.
Treatment: If symptomatic, treatment may involve surgical removal or endoscopic procedures.
d. Esophageal Fibroma
Definition: A rare benign tumor composed of fibrous tissue.
Symptoms: Typically, esophageal fibromas do not cause symptoms, but large ones may cause dysphagia or a sensation of fullness in the chest.
Treatment: Surgical removal may be necessary if the tumor causes significant symptoms.
3. Precursor Lesions (Non-Invasive)
Barrett’s Esophagus: A condition in which the normal squamous epithelium of the esophagus is replaced by columnar epithelium, often due to chronic acid reflux (GERD). It increases the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Dysplasia: Abnormal cell growth that can occur in Barrett’s esophagus or other esophageal conditions. It is considered a precursor to cancer and may lead to invasive esophageal carcinoma if untreated.
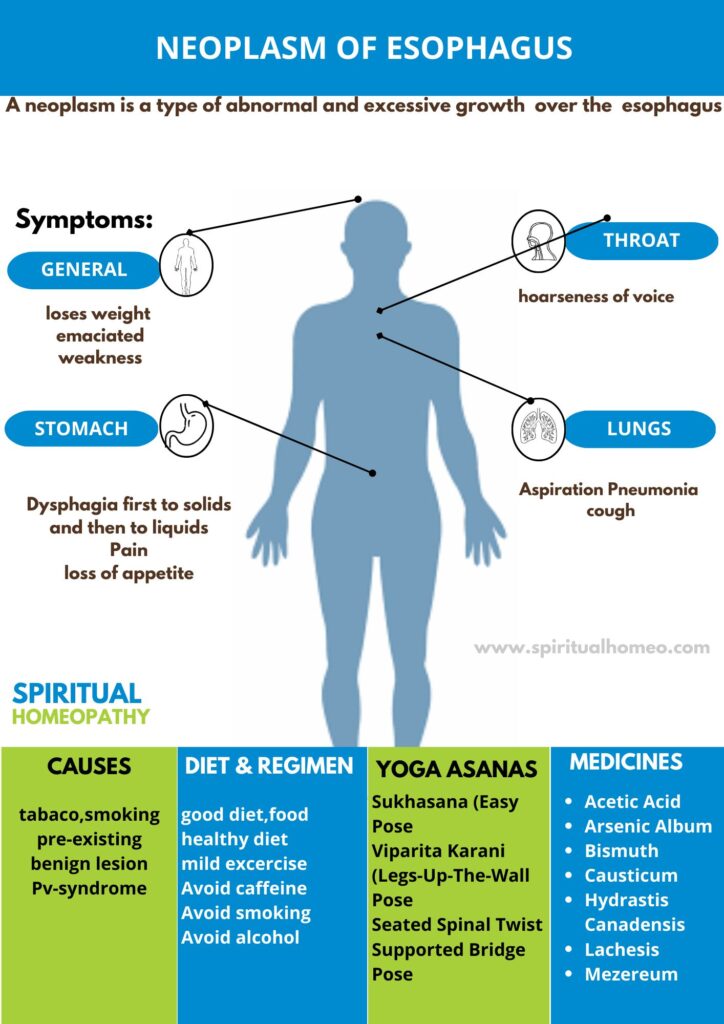
- Early symptoms. They include substernal discomfort and preference for soft or liquid food.
- Progressive dysphagia and emaciation. Dysphagia first to solids and then to liquids. Patient loses weight and becomes emaciated.
- Pain. Usually signifies extension of tumor beyond the walls of esophagus. It is referred to the back.
- Aspiration problem. Spread of cancer may cause laryngeal paralysis or fistulae formation leading to cough, hoarseness of voice, aspiration pneumonia and mediastinitis.
A neoplasm of the esophagus, commonly referred to as esophageal cancer, can have significant impacts on a person’s ability to swallow and digest food. Nutritional needs for people with esophageal neoplasm focus on maintaining proper nutrition, managing symptoms (like difficulty swallowing, nausea, or pain), and supporting the body during treatment.
Here’s an overview of what to eat for someone with esophageal cancer or an esophageal neoplasm, keeping in mind that diet should always be tailored to the individual and discussed with a healthcare provider or dietitian.
General Dietary Guidelines for Esophageal Cancer:
Easily Digestible Foods:
Since swallowing may become difficult, it’s essential to focus on foods that are easy to swallow and don’t irritate the esophagus.Soft or Pureed Foods: Pureed vegetables, mashed potatoes, applesauce, scrambled eggs, or smoothies.
Moist Foods: Incorporating sauces, gravies, broths, or yogurt can help make foods more manageable.
Cooked Vegetables: Steamed or well-cooked vegetables, which are softer and easier to swallow, are often more tolerable than raw vegetables.
Small, Frequent Meals:
Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help prevent feelings of fullness and reduce the risk of discomfort or reflux.Meals Every 2-3 Hours: Rather than eating large meals, try eating every 2 to 3 hours to ensure adequate nutrition and avoid overwhelming the digestive system.
High-Calorie, Nutrient-Dense Foods:
Esophageal cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation, can cause weight loss and decreased appetite. Eating high-calorie foods can help maintain energy and support weight management.Examples: Nut butters (peanut butter, almond butter), whole-milk dairy, avocados, hummus, full-fat Greek yogurt, and protein smoothies.
Hydration:
Staying hydrated is essential, especially if difficulty swallowing liquids is a concern.Examples: Water, herbal teas, clear broths, and smoothies.
Avoid: Carbonated drinks and caffeinated beverages, which may cause bloating or discomfort.
Protein-Rich Foods:
Protein helps maintain muscle mass, especially during cancer treatments. Soft or liquid protein sources may be easier to swallow.Examples: Eggs, tofu, soft fish, poultry (shredded), smooth nut butters, milkshakes, and protein powders.
Avoid Irritants:
Some foods can irritate the esophagus, especially if there is esophageal inflammation or sores from treatment. It’s important to avoid spicy, acidic, or rough-textured foods.Avoid: Spicy foods, acidic foods (like citrus, tomatoes), hard or dry foods (such as nuts, chips, and toast), and alcohol.
foods.
- junk food
- fast food
For individuals with a neoplasm of the esophagus (esophageal cancer), maintaining proper nutrition is crucial for managing symptoms, supporting the body during treatment, and improving overall health. A well-balanced, tailored diet and regimen can help individuals cope with difficulties in swallowing, nausea, and the side effects of treatments like chemotherapy and radiation.
Here’s an overview of a diet and regimen for someone with esophageal neoplasm:
Dietary Guidelines for Esophageal Cancer (Neoplasm of the Esophagus)
Key Principles:
Focus on Soft, Easily Swallowed Foods:
Esophageal cancer can make swallowing difficult, so it is essential to eat foods that are soft, moist, and easy to chew and swallow.Examples: Smooth soups, mashed potatoes, well-cooked vegetables, scrambled eggs, oatmeal, and smoothies.
High-Calorie, High-Protein Foods:
Weight loss is a common concern due to poor food intake, especially with chemotherapy or radiation. Focus on nutrient-dense, high-calorie foods to help maintain body weight and energy levels.Examples: Full-fat dairy, nut butters, avocados, creamy soups, and protein-rich smoothies.
Small, Frequent Meals:
Large meals can make swallowing more difficult and lead to discomfort. Eating smaller, more frequent meals helps ensure adequate nutrient intake while reducing strain on the digestive system.Suggestion: Try eating 5-6 small meals a day instead of 3 large ones.
Hydration:
Staying hydrated is essential, but if swallowing liquids is difficult, focus on liquids that are easy to drink and do not cause irritation.Examples: Water, clear broth, herbal tea, smoothies, and diluted fruit juices.
Avoid: Carbonated drinks, caffeinated beverages, and alcohol, which can irritate the esophagus.
Soft and Moist Foods:
Moisture is key to making food easier to swallow. Adding sauces, gravies, or broths to meals can help make food easier to digest.Examples: Mashed potatoes with gravy, moist meatballs, pureed soups, yogurt, and custards.
Avoid Irritating Foods:
Some foods may irritate the esophagus or worsen symptoms like heartburn or acid reflux.Avoid: Spicy foods, acidic foods (like citrus and tomatoes), rough-textured foods (such as dry crackers and bread), and foods that are overly hot or cold.
Foods to Include in the Diet for Esophageal Neoplasm:
1. Smoothies and Shakes:
Why: They provide a great way to get a high-calorie, protein-rich meal that is easy to swallow.
Examples: Blended fruits, yogurt, almond milk, protein powder, peanut butter, avocado, or oatmeal.
2. Pureed or Soft-Cooked Vegetables:
Why: Soft vegetables are easier to swallow and are packed with vitamins and minerals.
Examples: Pureed carrots, sweet potatoes, squash, and cooked spinach.
3. Soft Proteins:
Why: Protein is essential for healing, and soft proteins can be easier to swallow.
Examples: Scrambled eggs, tofu, soft fish (like salmon or cod), chicken cooked until tender, or well-cooked beans and lentils.
4. Creamy Soups and Broths:
Why: Soups are easy to swallow and can be packed with nutrition.
Examples: Pureed soups such as potato leek soup, creamy tomato soup, or chicken broth with soft vegetables.
5. Dairy Products:
Why: Dairy provides both protein and calcium. Soft dairy foods are easy to consume and can add calories.
Examples: Full-fat yogurt, cottage cheese, milkshakes, or smoothies with dairy-based ingredients.
6. Soft Grains:
Why: Soft grains are easily digestible and provide fiber, which aids in digestion.
Examples: Cream of wheat, oatmeal, white rice, or soft pasta.
Foods to Avoid:
Spicy Foods:
These can irritate the esophagus and cause discomfort.
Avoid: Chili, hot peppers, spicy curry, or dishes with strong spices.
Acidic Foods:
Foods with high acidity can irritate the lining of the esophagus and cause heartburn or reflux.
Avoid: Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons), tomatoes, vinegar, and pickled foods.
Hard or Dry Foods:
These foods are hard to swallow and may cause irritation or difficulty in chewing.
Avoid: Nuts, chips, dry bread, and crackers.
Alcohol and Caffeine:
Both alcohol and caffeine can irritate the esophagus and may interfere with treatment or digestion.
Avoid: Coffee, alcoholic beverages, sodas, and energy drinks.
Carbonated Beverages:
Carbonation can cause bloating or discomfort, especially if swallowing is difficult.
Avoid: Soda, sparkling water, and carbonated juices.
Sample Meal Plan for Esophageal Neoplasm:
Breakfast:
Smoothie: Blend banana, spinach, Greek yogurt, protein powder, and almond milk.
Scrambled eggs with a bit of cheese and soft, mashed avocado.
Lunch:
Pureed Carrot Soup with a side of soft mashed potatoes.
A small serving of soft tofu with some well-cooked spinach.
Snack:
A small bowl of Greek yogurt with honey and blended soft berries.
A protein shake or high-calorie smoothie with almond butter and protein powder.
Dinner:
Baked fish (salmon), tender and moist, with pureed butternut squash.
Creamy mashed sweet potatoes or white rice with a mild, non-acidic gravy.
Evening Snack:
Custard or pudding.
Soft scrambled eggs or rice pudding.
Exercise and Physical Activity Regimen for Esophageal Cancer:
In addition to a proper diet, a balanced exercise regimen can support overall health, improve energy levels, and reduce fatigue, which is common in cancer patients.
Light Activity:
Walking: Short walks after meals can help digestion and improve energy levels.
Stretching: Gentle stretching or yoga can reduce stress and improve flexibility.
Strengthening Exercises:
Light strength training with resistance bands or bodyweight exercises like squats or wall push-ups can maintain muscle mass.
Breathing Exercises:
Deep breathing exercises can help reduce anxiety and improve oxygen flow to the body, which is important during treatment.
Why Choose Homeopathy?
Homeopathy offers natural and holistic healing, treating the root cause of ailments without side effects. It strengthens the body’s defense system, is gentle for all ages, and personalized to each individual’s needs. Choose homeopathy for safe, effective, and long-lasting health solutions.
Spiritual Homeopathy: Your Path to Natural Healing
At Spiritual Homeopathy, where we believe in the power of holistic healing and personalized care. Our mission is to provide compassionate and effective homeopathic treatment to help you achieve optimal health and well-being. With a focus on addressing the root cause of illness and promoting harmony between mind, body, and spirit, we are dedicated to guiding you on your journey towards vibrant health and vitality.
Why Choose Spiritual Homeopathy?
At Spiritual Homeopathy, we offer a unique approach to healing that integrates traditional homeopathic principles with a deep understanding of the spiritual aspects of health. Our team of experienced homeopathic practitioners combines expertise with empathy, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care tailored to your individual needs.
Our Approach to Treatment
We believe that true healing occurs when all aspects of a person—physical, emotional, and spiritual—are in balance. That’s why our treatment approach goes beyond simply addressing symptoms to identify and treat the underlying imbalances contributing to your health concerns. By addressing the root cause of illness and supporting your body’s innate healing ability, we empower you to achieve lasting health and vitality.
Services We Offer
Consultations: Our experienced best homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad offer comprehensive consultations to assess your health concerns, medical history, and individual needs.we also take online consultation and We take the time to listen to your story, understand your unique health goals, and develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Remedies: At Spiritual Homeopathy, we provide a wide range of homeopathic remedies carefully selected to address a variety of health conditions. From acute ailments to chronic diseases, our remedies are safe, gentle, and effective, offering natural relief without the side effects often associated with conventional medications.
Follow-Up Care: We believe in the importance of ongoing support and monitoring throughout your healing journey. Our team is dedicated to providing regular follow-up care to track your progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that you are on the path to optimal health and well-being.
Our Commitment to You
At Spiritual Homeopathy, your health and wellness are our top priorities. We are committed to providing you with compassionate care, personalized treatment, and the support you need to achieve your health goals. Whether you are seeking relief from a specific health concern or simply looking to optimize your overall well-being, we are here to support you every step of the way.
What is Neoplasm of Esophagus?
A neoplasm is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. In addition; The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Neoplasm of Esophagus?
- Acetic Acid
- Arsenic Album
- Bismuth
- Causticum
- Hydrastis Canadensis
- Lachesis
- Mezereum
- Spigelia
What causes Neoplasm of Esophagus?
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
- Tobacco chewing and smoking
- Benign strictures, hiatus hernia, cardiac achalasia and diverticula.
- Plummer–Vinson syndrome
What are the symptoms of Neoplasm of Esophagus?
- Substernal discomfort and preference for soft or liquid food
- Progressive dysphagia and emaciation
- Pain
- Aspiration problem
Reference
[1]Diseases_of_Ear_Nose_and_Throat_6Edition
[2]https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=34&ContentID=17970-1
[3] Homoeopathic Therapeutics by Lilienthal